Example for Configuring an OSPF NSSA
This section describes how to configure an OSPF not-so-stubby area (NSSA).
Networking Requirements
An excessive number of entries in a routing table wastes network resources and causes high CPU usage. To solve this problem, a non-backbone area on the border of an AS can be configured as an NSSA to reduce the amount of routing information to be transmitted. An NSSA in an AS does not transmit routes learned from other areas in the AS but imports AS external routes. This reduces bandwidth and storage resource consumption.
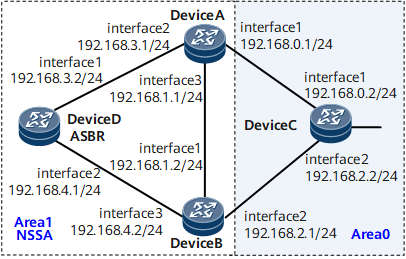
On the network shown in Figure 1, OSPF runs on all routers and the entire AS is divided into two areas. Device A and Device B function as Area Border Routers (ABRs) to forward inter-area routes; Device D functions as an Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR) and imports the external static route 10.0.0.0/8. To import AS-external routes but reduce the number of Link State Advertisements (LSAs) advertised to area 1 without affecting route reachability, configure area 1 as an NSSA and configure Device A as an LSA translator in the NSSA.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Enable OSPF on all routers and configure basic OSPF functions to ensure that routers communicate with each other using OSPF. For details, see Configuring Basic OSPF Functions.
- Configure area 1 as an NSSA.
- Configure Device D to import the static route 10.0.0.0/8.
- Configure Device A in the NSSA as an LSA translator.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
- Router ID 1.1.1.1 of Device A; OSPF process ID 1; network segment 192.168.0.0/24 of area 0; network segments 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.3.0/24 of area 1
- Router ID 2.2.2.2 of Device B; OSPF process ID 1; network segment 192.168.2.0/24 of area 0; network segments 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.4.0/24 of area 1
- Router ID 3.3.3.3 of Device C; OSPF process ID 1; network segments 192.168.0.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24 of area 0
- Router ID 4.4.4.4 of Device D; OSPF process ID 1; network segments 192.168.3.0/24 and 192.168.4.0/24 of area 1
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each interface.
Configure an IP address for each interface as shown in Figure 1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure basic OSPF functions.
Configuring Basic OSPF Functions shows how to configure basic OSPF functions. For details about the configuration, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure area 1 as an NSSA.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] ospf [*DeviceA-ospf-1] area 1 [*DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] nssa [*DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] commit [~DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] ospf [*DeviceB-ospf-1] area 1 [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] nssa [*DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] commit [~DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] quit
# Configure Device D.
[~DeviceD] ospf [*DeviceD-ospf-1] area 1 [*DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] nssa [*DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] commit [~DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] quit
- Configure Device D to import the static route 10.0.0.0/8.
[*DeviceD] ip route-static 10.0.0.0 8 null 0 [*DeviceD] ospf [*DeviceD-ospf-1] import-route static [*DeviceD-ospf-1] commit [~DeviceD-ospf-1] quit
# Display the OSPF routing table on Device C.
[~DeviceC] display ospf routing OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 3.3.3.3 Routing Tables Routing for Network Destination Cost Type NextHop AdvRouter Area 192.168.3.0/24 2 Inter-area 192.168.0.1 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 192.168.4.0/24 2 Inter-area 192.168.2.1 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.0/24 1 Stub 192.168.0.2 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.0/24 2 Inter-area 192.168.0.1 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.0/24 2 Inter-area 192.168.2.1 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0/24 1 Stub 192.168.2.2 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 Routing for ASEs Destination Cost Type Tag NextHop AdvRouter 10.0.0.0/8 1 Type2 1 192.168.2.1 2.2.2.2 Total Nets: 7 Intra Area: 2 Inter Area: 4 ASE: 1 NSSA: 0
The command output shows that Device B has imported an AS external route and that the router ID of the router that advertises the imported AS external route is 2.2.2.2. Device B functions as the type-5 LSA translator because OSPF selects the ABR with a larger router ID as an LSA translator.
- # Configure Device A as an LSA translator.
[~DeviceA] ospf [*DeviceA-ospf-1] area 1 [*DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] nssa default-route-advertise no-summary translator-always [*DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] commit [~DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# View the OSPF routing table on Device C.
[~DeviceC] display ospf routing OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 3.3.3.3 Routing Tables Routing for Network Destination Cost Type NextHop AdvRouter Area 192.168.3.0/24 2 Inter-area 192.168.0.1 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 192.168.4.0/24 2 Inter-area 192.168.2.1 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.0/24 1 Stub 192.168.0.2 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.0/24 2 Inter-area 192.168.2.1 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.0/24 2 Inter-area 192.168.0.1 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0/24 1 Stub 192.168.2.2 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 Routing for ASEs Destination Cost Type Tag NextHop AdvRouter 10.0.0.0/8 1 Type2 1 192.168.0.1 1.1.1.1 Total Nets: 7 Intra Area: 2 Inter Area: 4 ASE: 1 NSSA: 0
The command output shows that Device C has imported an AS external route and that the router ID of the router that advertises the imported AS external route is 1.1.1.1. Device A functions as the type-5 LSA translator.
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # router id 1.1.1.1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0.0.0.1 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 nssa default-route-advertise no-summary translator-always # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # router id 2.2.2.2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.4.2 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0.0.0.1 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 nssa # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # router id 3.3.3.3 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.0.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # router id 4.4.4.4 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.3.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.4.1 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 import-route static area 0.0.0.1 network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 nssa # ip route-static 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 NULL0 # return