Understanding PADS
PADS
The PADS simulates experts to monitor the service status in real time and automatically diagnoses and recovers faults.
The PADS provides the following functions:
Self-diagnosis and self-recovery of specific fault modes
Service health checks and self-recovery of poor check results
The service health checks include:
- Abnormal service status check: Diagnostic logs are recorded. The status of the latest abnormal services can be queried using commands.
- In-process service status check: Diagnostic information is recorded in the PADS O&M file on the PADS-dedicated CF card. The information can be used to restore the service status on site.
Implementation
Figure 1 Implementation of the PADS
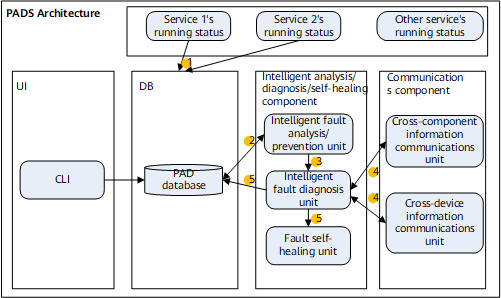

- Each service saves the service status in real time to the PADS O&M file on the CF card. Key information is backed up in the memory for analysis.
- The intelligent fault analysis/prevention unit monitors the running status data of each service in real time.
- The intelligent fault diagnosis unit starts end-to-end automatic diagnosis after detecting an exception. You can also run diagnostic commands to start end-to-end fault analysis.
- In the diagnosis process, if information needs to be collected and analyzed across components and devices, use the cross-component and cross-device communications capability provided by the PADS.
- Diagnosis results can be queried by running commands at any time. If any fault in the diagnosis results needs to be self-healed, the PADS interworks with the self-healing system to complete fault self-healing.