Summary of QinQ Configuration Tasks
This section describes the QinQ features supported by the NetEngine 8000 F in terms of the QinQ configuration.
- A QinQ-enabled device is capable of virtual local area network (VLAN) stacking, which expands VLAN space and reduces the consumption of VLAN ID resources. If selective QinQ is configured, the device can add different outer VLAN tags to packets and transmit the packets.
QinQ supports the following features that meet different configuration requirements:
- Configuring QinQ-based VLAN tag swapping: The device can swap the inner tag with the outer tag in a double-tagged packet.
- Configuring QinQ mapping: The device can map the user VLAN ID in a packet to a carrier VLAN ID.
- Configuring VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces to transmit IP services: Proxy Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) (DHCP server/DHCP relay), and Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) can be configured on sub-interfaces for QinQ/dot1q VLAN tag termination.
- Configuring VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces to transmit virtual private network (VPN) services: The L2VPN (VPWS/VPLS) and L3VPN can be configured on sub-interfaces for QinQ/dot1q VLAN tag termination.
- Configuring QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces to support 802.1p mappings: The mappings include the 802.1p-to-DSCP mapping and 802.1p-to-MPLS-EXP mapping.
- Configuring L2VPN access on QinQ stacking sub-interfaces: With this configuration, QinQ stacking sub-interfaces can implement L2VPN (VPWS/VPLS).
- QinQ stacking sub-interfaces can be used to solve the problem that one physical interface cannot provide L2VPN access for multiple users.
Access Services Provided by VLAN Tag Termination Sub-Interfaces
Sub-interfaces for QinQ/dot1q VLAN tag termination support IP services (for example, proxy ARP, DHCP, and VRRP), VPN services (for example, L2VPN and L3VPN), 802.1p-to-DSCP mapping, and 802.1p-to-MPLS-EXP mapping. Table 1 shows the application scenario of a VLAN tag termination sub-interface providing access services.
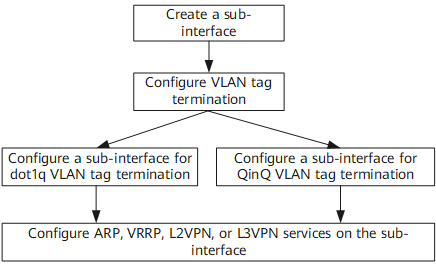
Figure 1 shows how to configure sub-interfaces for QinQ/dot1q VLAN tag termination.
Differences Between the VLAN Tag Termination Sub-Interface and Dot1q Sub-Interface
Table 2 shows the differences between the VLAN tag termination sub-interface and dot1q sub-interface.
Interface Type |
Supported VPN Service |
Description |
Difference |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VPWS (CCC mode) |
VPWS |
VPLS |
L3VPN |
|||
Dot1q sub-interface |
Supported |
Supported |
Supported |
Supported |
You can run the vlan-type dot1q command to configure an Ethernet sub-interface to be a dot1q sub-interface. |
|
Dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface |
Supported |
Supported |
Supported |
Supported |
You can run the dot1q termination vid command to configure a dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface to terminate single-tagged packets. NOTE:
|
|
QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interface |
Supported |
Supported |
Supported |
Supported |
You can run the qinq termination pe-vid ce-vid command to configure a QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interface to terminate double-tagged packets. NOTE:
You can run the qinq termination l2 command to configure the asymmetrical or symmetrical mode. |
|
Table 3 and Table 4 show how different types of interfaces process VLAN tags carried in packets to be transmitted across a VPLS network.
Inbound Interface Type |
Packet Processing for VPLS Network Access |
|
|---|---|---|
Ethernet-Encapsulated Packets |
VLAN-Encapsulated Packets |
|
Dot1q sub-interface |
Tags are stripped. |
No action is performed. |
Dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface |
Tags are stripped. |
No action is performed. |
QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interface |
|
|
QinQ stacking sub-interface |
The outer tag is added. |
The outer tag is added. |
QinQ mapping sub-interface |
The outer tag is replaced. |
The outer tag is replaced. |
Outbound Interface Type |
Packet Processing for VPLS Network Access |
|
|---|---|---|
Ethernet-Encapsulated Packets |
VLAN-Encapsulated Packets |
|
Dot1q sub-interface |
A specific tag is added. |
The tag is replaced. |
Dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface |
A specific tag is added. |
The tag is replaced. |
QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interface |
|
|
QinQ stacking sub-interface |
The outer tag is stripped. |
The outer tag is stripped. |
QinQ mapping sub-interface |
The outer tag is replaced. |
The outer tag is replaced. |

-
Each Ethernet frame transmitted between CEs and PEs carries a VLAN tag called a Provider-Tag (P-tag). The tag is a service delimiter required by a carrier for user differentiation.
-
Ethernet frames transmitted between CEs and PEs do not necessarily carry VLAN tags. If an Ethernet frame carries a VLAN tag, the tag is an internal VLAN tag called a User-Tag (U-tag) in user packets. The U-tag is carried in a packet before the packet is sent to a CE. The U-tag is used by the CE to identify the packet, but PEs do not recognize U-tags.
By default, the encapsulation type is VLAN.