Configuring Inter-AS Seamless MPLS+HVPN
In the inter-AS seamless MPLS+HVPN networking, an HVPN between each CSG and AGG is configured, and inter-AS seamless MPLS is configured for the link between each AGG and MASG. The networking integrates the seamless MPLS and HVPN advantages.
Usage Scenario
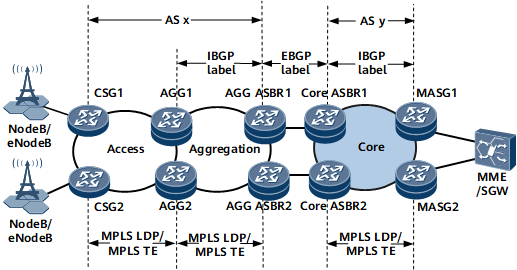
Figure 1 illustrates the inter-AS seamless MPLS+HVPN networking. A Cell Site Gateway (CSG) and an Aggregation (AGG) establish an HVPN connection, and the AGG and a Mobile Aggregate Service Gateway (MASG) establish a seamless MPLS LSP. The AGG hierarchically provides L3VPN access services and routing management services. Seamless MPLS+HVPN combines the advantages of both MPLS and HVPN. Seamless MPLS allows any two nodes on an inter-AS LSP to transmit services at the access, aggregation, and core layers, providing high service scalability. HVPN enables carriers to cut down network deployment costs by deploying devices with layer-specific capacities to meet service requirements.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring inter-AS seamless MPLS+HVPN, complete the following tasks:
Configure IGP protocols to implement connectivity at the access, aggregation, and core layers and enable MPLS LDP or MPLS TE to implement MPLS forwarding on a public network.
Configure an EBGP peer relationship between each pair of an AGG ASBR and core ASBR and an IBGP peer relationship between each pair of the following nodes:
- CSG and AGG
- AGG and AGG ASBR
- Core ASBR and MASG
Configure an HVPN between each pair of a CSG and AGG.

If MPLS TE tunnels are used across the three layers, a tunnel policy or tunnel selector must be configured. For configuration details, see VPN Tunnel Management Configuration.
- Establishing an MP-EBGP Peer Relationship Between Each AGG and MASG
- MP-EBGP supports BGP extended community attributes that are used to advertise VPNv4 routes between each pair of the AGG and MASG.
- Enabling BGP Peers to Exchange Labeled IPv4 Routes
- In the inter-AS seamless MPLS+HVPN networking, before an E2E BGP LSP is established between an AGG and MASG, these two BGP peers must be able to exchange labeled IPv4 routes with each other.
- Configuring a BGP LSP
- Before a BGP LSP is established, a routing policy must be configured to control label distribution. The egress of the BGP LSP to be established needs to assign an MPLS label to the route advertised to an upstream node. If a transit node receives a labeled IPv4 route from downstream, the downstream node must re-assign an MPLS label to the transit node and advertises the label upstream.
- (Optional) Configuring the Mode in Which a BGP Label Inherits the QoS Priority in an Outer Tunnel Label
- When data packets are transmitted from a core ASBR to an AGG ASBR, you can determine whether a BGP label inherits the QoS priority carried in an outer tunnel label.
- (Optional) Configuring the Protection Switching Function
- A protection switching function, such as link or node protection, can be configured to provide high availability for an inter-AS seamless MPLS+HVPN network.
- (Optional) Configuring the Egress Protection Function
- The egress protection function reduces E2E BFD sessions to be established, bandwidth resources to be consumed, and the burden on devices.
- Verifying the Configuration of Inter-AS Seamless MPLS+HVPN
- After configuring inter-AS seamless MPLS+HVPN, you can check all BGP peer relationships, VPNv4 routing information on AGGs and MASGs, and the connectivity of the BGP LSP between each pair of an AGG and MASG.