Example for Configuring Dynamic BFD to Monitor a BGP Tunnel
This section provides an example for configuring dynamic BFD to monitor a BGP tunnel. The configuration involves configuring a BGP tunnel and configuring dynamic BFD for BGP tunnel.
Networking Requirements
Seamless MPLS integrates the access, aggregation, and core layers on the same MPLS network to transmit VPN services. Seamless MPLS establishes an E2E BGP tunnel to provide E2E access services. To rapidly detect faults in BGP tunnels, BFD for BGP tunnel needs to be configured.
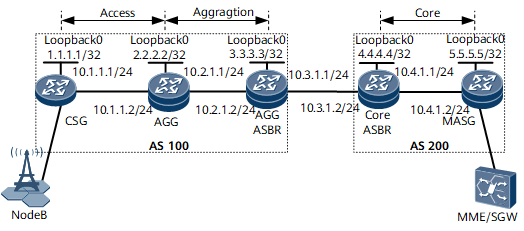
In Figure 1, the access and aggregation layers belong to one AS, and the core layer belongs to another AS. NodeBs need to communicate with an MME or SGW over a VPN. To meet this requirement, inter-AS seamless MPLS can be configured between the CSG and MASG. To monitor the connectivity of the BGP tunnel, BFD for BGP tunnel needs to be configured.
Device Name |
Interface Name |
IP Address and Mask |
|---|---|---|
CSG |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
AGG |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.2.1.1/24 |
|
AGG ASBR |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.2.1.2/24 |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.3.1.1/24 |
|
Core ASBR |
GE 0/1/0 |
10.3.1.2/24 |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.4.1.1/24 |
|
MASG |
GE 0/1/8 |
10.4.1.2/24 |
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure inter-AS seamless MPLS.
Configure BFD for BGP tunnel.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
OSPF process ID (1) at the access layer, IS-IS process ID (1) at the aggregation layer, and OSPF process ID (2) at the core layer
IS-IS area number (10.0001) and IS-IS system IDs (which are obtained based on loopback0 addresses)
MPLS LSR IDs: 1.1.1.1 for the CSG, 2.2.2.2 for the AGG, 3.3.3.3 for the AGG ASBR, 4.4.4.4 for the core ASBR, and 5.5.5.5 for the MASG
Name of a routing policy (policy1)
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface.
Assign an IP address and mask to each interface, including each loopback interface, according to Figure 1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure an IGP.
Configure OSPF with process ID 1 at the access layer, IS-IS with process ID 1 at the aggregation layer, and OSPF with process ID 2 at the core layer. Configure IGP protocols to advertise the route to each network segment to which each interface is connected and to advertise the host route to each loopback address which is used as an LSR ID. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure basic MPLS and MPLS LDP functions.
Enable MPLS and MPLS LDP globally on each device and on interfaces in each AS. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Establish IBGP peer relationships at each layer and enable devices to exchange labeled routes.
# Configure the CSG.
[~CSG] bgp 100 [*CSG-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 [*CSG-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [*CSG-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 label-route-capability [*CSG-bgp] network 1.1.1.1 32 [*CSG-bgp] quit [*CSG] commit
# Configure the AGG.
[~AGG] bgp 100 [*AGG-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 [*AGG-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [*AGG-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 label-route-capability [*AGG-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 [*AGG-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [*AGG-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 label-route-capability [*AGG-bgp] quit [*AGG] commit
# Configure the AGG ASBR.
<AGG ASBR> system-view [~AGG ASBR] bgp 100 [*AGG ASBR-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 [*AGG ASBR-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [*AGG ASBR-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 label-route-capability [*AGG ASBR-bgp] quit [*AGG ASBR] commit
# Configure the core ASBR.
<Core ASBR> system-view [~Core ASBR] bgp 200 [*Core ASBR-bgp] peer 5.5.5.5 as-number 200 [*Core ASBR-bgp] peer 5.5.5.5 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [*Core ASBR-bgp] peer 5.5.5.5 label-route-capability [*Core ASBR-bgp] quit [*Core ASBR] commit
# Configure the MASG.
[~MASG] bgp 100 [*MASG-bgp] peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 100 [*MASG-bgp] peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [*MASG-bgp] peer 4.4.4.4 label-route-capability [*MASG-bgp] network 5.5.5.5 32 [*MASG-bgp] quit [*MASG] commit
- Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the AGG ASBR and core ASBR and enable these devices to exchange labeled routes.
# Configure the AGG ASBR.
[~AGG ASBR] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/8 [~AGG ASBR-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.3.1.1 24 [*AGG ASBR-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls [*AGG ASBR-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*AGG ASBR] bgp 100 [*AGG ASBR-bgp] peer 10.3.1.2 as-number 200 [*AGG ASBR-bgp] peer 10.3.1.2 label-route-capability check-tunnel-reachable [*AGG ASBR-bgp] quit [*AGG ASBR] commit
# Configure the core ASBR.
[~Core ASBR] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [~Core ASBR-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.3.1.2 24 [*Core ASBR-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*Core ASBR-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*Core ASBR] bgp 200 [*Core ASBR-bgp] peer 10.3.1.1 as-number 100 [*Core ASBR-bgp] peer 10.3.1.1 label-route-capability check-tunnel-reachable [*Core ASBR-bgp] quit [*Core ASBR] commit
- Configure each AGG as an RR to help the CSG and MASG obtain the route destined for each other's loopback interface.
# Configure the AGG.
[~AGG] bgp 100 [~AGG-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 reflect-client [*AGG-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 next-hop-local [*AGG-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 reflect-client [*AGG-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 next-hop-local [*AGG-bgp] quit [*AGG] commit
- Configure a routing policy on each device to establish a BGP LSP in a BGP tunnel.
# Configure a routing policy for advertising routes matching Route-Policy conditions to the CSG's BGP peer.
[~CSG] route-policy policy1 permit node 1 [*CSG-route-policy] apply mpls-label [*CSG-route-policy] quit [*CSG] bgp 100 [*CSG-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 route-policy policy1 export [*CSG-bgp] quit [*CSG] commit
Repeat this step for the MASG. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
# Configure a routing policy for advertising routes matching Route-Policy conditions to the AGG's BGP peer.
[~AGG] route-policy policy1 permit node 1 [*AGG-route-policy] if-match mpls-label [*AGG-route-policy] apply mpls-label [*AGG-route-policy] quit [*AGG] bgp 100 [*AGG-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 route-policy policy1 export [*AGG-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 route-policy policy1 export [*AGG-bgp] quit [*AGG] commit
Repeat this step for the AGG ASBR and core ASBR. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure BFD for BGP tunnel.
# On the CSG, enable the MPLS capability to dynamically establish BGP BFD sessions based on host addresses.
[~CSG] bfd [*CSG-bfd] quit [*CSG] mpls [*CSG-mpls] mpls bgp bfd enable [*CSG-mpls] mpls bgp bfd-trigger-tunnel host [*CSG-mpls] quit [*CSG] commit
# On the MASG, enable the MPLS capability of passively creating a BFD session.
[~MASG] bfd [*MASG-bfd] mpls-passive [*MASG-bfd] quit [*MASG] commit
- Verify the configuration.
After completing the preceding configurations, run the display mpls bfd session command on the CSG to view information about the BFD session that monitors a BGP tunnel.
[~CSG] display mpls bfd session protocol bgp ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- BFD Information: BGP TUNNEL ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FEC DISC OUT-IF NEXTHOP TUNNEL STATE ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5.5.5.5 16385 - -.-.-.- - Up
Configuration Files
CSG configuration file
# sysname CSG # bfd # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls mpls bgp bfd enable mpls bgp bfd-trigger-Tunnel host # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast network 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 2.2.2.2 route-policy policy1 export peer 2.2.2.2 label-route-capability # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 apply mpls-label # returnAGG configuration file
# sysname AGG # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls # mpls ldp # isis 1 network-entity 10.0001.0020.0200.2002.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast peer 1.1.1.1 enable peer 1.1.1.1 route-policy policy1 export peer 1.1.1.1 reflect-client peer 1.1.1.1 next-hop-local peer 1.1.1.1 label-route-capability peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 3.3.3.3 route-policy policy1 export peer 3.3.3.3 reflect-client peer 3.3.3.3 next-hop-local peer 3.3.3.3 label-route-capability # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 if-match mpls-label apply mpls-label # return
AGG ASBR configuration file
# sysname AGG ASBR # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls # mpls ldp # isis 1 network-entity 10.0001.0030.0300.3003.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls # interface LoopBack0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.3.1.2 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 2.2.2.2 route-policy policy1 export peer 2.2.2.2 label-route-capability peer 10.3.1.2 enable peer 10.3.1.2 route-policy policy1 export peer 10.3.1.2 label-route-capability check-tunnel-reachable # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 if-match mpls-label apply mpls-label # return
Core ASBR configuration file
# sysname Core ASBR # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 # bgp 200 peer 5.5.5.5 as-number 200 peer 5.5.5.5 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 10.3.1.1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast peer 5.5.5.5 enable peer 5.5.5.5 route-policy policy1 export peer 5.5.5.5 label-route-capability peer 10.3.1.1 enable peer 10.3.1.1 route-policy policy1 export peer 10.3.1.1 label-route-capability check-tunnel-reachable # ospf 2 area 0.0.0.0 network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255 # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 if-match mpls-label apply mpls-label # return
MASG configuration file
# sysname MASG # bfd mpls-passive # mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.5 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255 # bgp 200 peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 200 peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast network 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255 peer 4.4.4.4 enable peer 4.4.4.4 route-policy policy1 export peer 4.4.4.4 label-route-capability # ospf 2 area 0.0.0.0 network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0 network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255 # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 apply mpls-label # return