SR-MPLS TE Load Balancing
SR-MPLS TE Load Balancing
SR-MPLS TE guides data packet forwarding based on the label stack information encapsulated by the ingress into data packets. By default, each adjacency label identifies a specific adjacency, meaning that load balancing cannot be performed even if equal-cost links exist. To address this issue, SR-MPLS TE uses parallel adjacency labels to identify multiple equal-cost links.
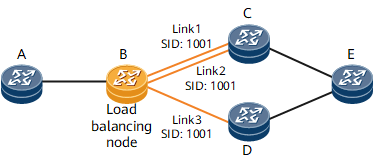
In Figure 1, there are three equal-cost links from nodes B to E. Adjacency SIDs with the same value, such as 1001 in Figure 1, can be configured for the links. Such SIDs are called parallel adjacency labels, which are also used for path computation like common adjacency labels.
When receiving data packets carrying parallel adjacency labels, node B parses the labels and uses the hash algorithm to load-balance the traffic over the three equal-cost links, improving network resource utilization and avoiding network congestion.
Configuring parallel adjacency labels does not affect the allocation of common adjacency labels between IGP neighbors. After parallel adjacency labels are configured, the involved device advertises multiple adjacency labels for the same adjacency.
If BFD for SR-MPLS TE is enabled and SR-MPLS TE parallel adjacency labels are used, BFD packets can be load-balanced, whereas each BFD packet is hashed to a single link. If the link fails, BFD may detect a link-down event even if the other links keep working properly. As a result, a false alarm may be reported.