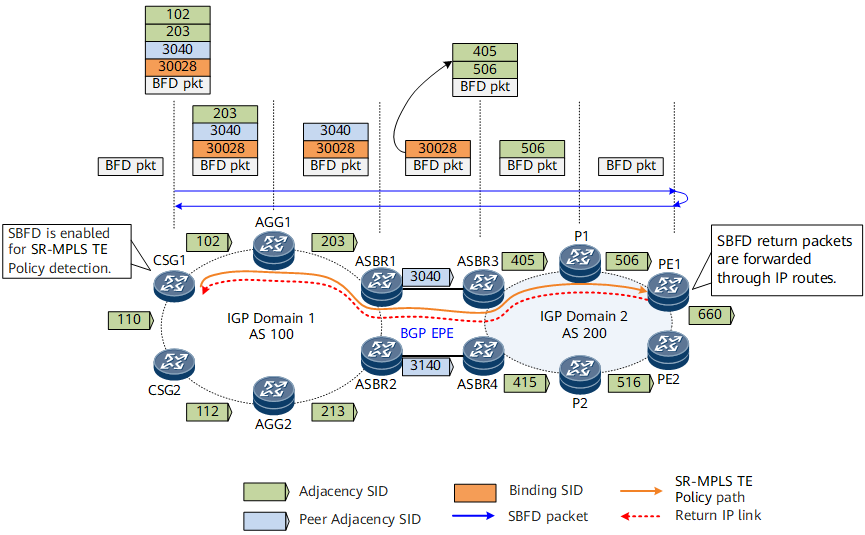
SBFD For SR-MPLS TE Policy
Unlike RSVP-TE, which exchanges Hello messages between forwarders to maintain tunnel status, an SR-MPLS TE Policy cannot maintain its status in the same way. An SR-MPLS TE Policy is established immediately after the headend delivers a label stack. The SR-MPLS TE Policy remains up only unless the label stack is revoked. Therefore, seamless bidirectional forwarding detection (SBFD) for SR-MPLS TE Policy is introduced for SR-MPLS TE Policy fault detection. SBFD for SR-MPLS TE Policy is an end-to-end fast detection mechanism that quickly detects faults on the link through which an SR-MPLS TE Policy passes.
- After SBFD for SR-MPLS TE Policy is enabled on the headend, the endpoint uses the endpoint address (IPv4 address only) as the remote discriminator of the SBFD session corresponding to the segment list in the SR-MPLS TE Policy by default. If multiple segment lists exist in the SR-MPLS TE Policy, the remote discriminators of the corresponding SBFD sessions are the same.
- The headend sends an SBFD packet encapsulated with a label stack corresponding to the SR-MPLS TE Policy.
- After the endpoint device receives the SBFD packet, it returns a reply through the shortest IP link.
- If the headend receives the reply, it considers that the corresponding segment list in the SR-MPLS TE Policy is normal. Otherwise, it considers that the segment list is faulty. If all the segment lists referenced by a candidate path are faulty, SBFD triggers a candidate path switchover.
SBFD return packets are forwarded over IP. If the primary paths of multiple SR-MPLS TE Policies between two nodes differ due to different path constraints but SBFD return packets are transmitted over the same path, a fault in the return path may cause all involved SBFD sessions to go down. As a result, all the SR-MPLS TE Policies between the two nodes go down. The SBFD sessions of multiple segment lists in the same SR-MPLS TE Policy also have this problem.
By default, if HSB protection is not enabled for an SR-MPLS TE Policy, SBFD detects all the segment lists only in the candidate path with the highest preference in the SR-MPLS TE Policy. With HSB protection enabled, SBFD can detect all the segment lists of candidate paths with the highest and second highest priorities in the SR-MPLS TE Policy. If all the segment lists of the candidate path with the highest preference are faulty, a switchover to the HSB path is triggered.