Example for Configuring EVPN L3VPNv4 over SRv6 BE Flex-Algo
This section provides an example for configuring EVPN L3VPNv4 over SRv6 BE Flex-Algo.
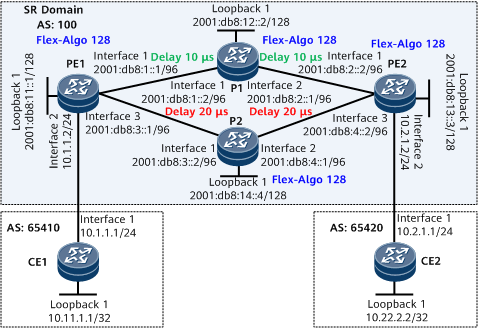
Networking Requirements
PE1, the Ps, and PE2 are in the same AS and run IS-IS to implement IPv6 network connectivity.
PE1, the Ps, and PE2 are Level-1 devices that belong to IS-IS process 1.
It is required that a bidirectional SRv6 BE path be deployed between PE1 and PE2 on the public network to carry EVPN L3VPNv4 services. Though PE1 and PE2 have multiple links in between, the service traffic needs to be forwarded over the PE1-P1-PE2 link with the lowest delay.
In this example, static delay attributes are defined to meet the service requirements of vpn1.
Precautions
When configuring EVPN L3VPNv4 over SRv6 BE Flex-Algo, note the following:
After a VPN instance is bound to a PE interface connected to a CE, Layer 3 configurations on this interface, such as IP address and routing protocol configurations, are automatically deleted. Add these configurations again if necessary.
To ensure that delay attributes can be transmitted between devices, you need to run the ipv6 traffic-eng command to enable IS-IS TE and the ipv6 metric-delay advertisement enable command to enable IPv6 delay advertisement.
- In SRv6 Flex-Algo scenarios, locators must be configured on both PEs and Ps, and IS-IS SRv6 must be enabled using the segment-routing ipv6 locator locator-name command in the IS-IS view. Otherwise, SRv6 locator routes cannot be advertised, and PEs at both ends cannot learn locator routes from each other.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure an IPv6 address for each interface on PE1, P1, PE2, and P2.
Enable IS-IS, configure an IS-IS level, and specify a network entity title (NET) on PE1, P1, PE2, and P2.
- Configure delay attributes for Flex-Algo links.
- Configure FADs.
- Enable IS-IS-based Flex-Algo advertisement, IS-IS TE, and IS-IS-based IPv6 link delay advertisement.
Configure VPN instances on PE1 and PE2.
Establish an EBGP peer relationship between each PE and its connected CE.
Establish a BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
- Establish a Flex-Algo-based SRv6 BE path between the PEs.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
IPv6 address of each interface on PE1, P1, PE2, and P2
IS-IS process IDs of PE1, P1, PE2, and P2
IS-IS levels of PE1, P1, PE2, and P2
VPN instance names, RDs, and RTs on PE1 and PE2
Procedure
- Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure an IPv6 address for each interface. The following example uses the configuration of PE1. The configurations of other devices are similar to the configuration of PE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ipv6 enable [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::1 96 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ipv6 enable [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ipv6 address 2001:db8:3::1 96 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE1] interface LoopBack 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 enable [*PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2001:db8:11::1 128 [*PE1-LoopBack1] quit [*PE1] commit
- Configure IS-IS.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1 [*PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide [*PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 [*PE1-isis-1] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*PE1-isis-1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE1] interface loopback1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] commit [~PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure P1.
[~P1] isis 1 [*P1-isis-1] is-level level-1 [*P1-isis-1] cost-style wide [*P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 [*P1-isis-1] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*P1-isis-1] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P1] interface loopback1 [*P1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*P1-LoopBack1] commit [~P1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] isis 1 [*PE2-isis-1] is-level level-1 [*PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide [*PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 [*PE2-isis-1] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*PE2-isis-1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE2] interface loopback1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] commit [~PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure P2.
[~P2] isis 1 [*P2-isis-1] is-level level-1 [*P2-isis-1] cost-style wide [*P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 [*P2-isis-1] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*P2-isis-1] quit [*P2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P2] interface loopback1 [*P2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*P2-LoopBack1] commit [~P2-LoopBack1] quit
After the configuration is complete, perform the following operations to check whether IS-IS is successfully configured:
# Display IS-IS neighbor information. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display isis peer Peer information for ISIS(1) System Id Interface Circuit Id State HoldTime Type PRI -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0000.0000.0002* GE0/1/0 0000.0000.0002.01 Up 6s L1 64 0000.0000.0004* GE0/1/16 0000.0000.0004.01 Up 9s L1 64 Total Peer(s): 2
# Display IS-IS routing table information. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display isis route Route information for ISIS(1) ----------------------------- ISIS(1) Level-1 Forwarding Table -------------------------------- IPV6 Dest. ExitInterface NextHop Cost Flags -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2001:DB8:1::/96 GE0/1/0 Direct 10 D/-/L/- 2001:DB8:2::/96 GE0/1/0 FE80::3A5D:67FF:FE31:307 20 A/-/-/- 2001:DB8:3::/96 GE0/1/16 Direct 10 D/-/L/- 2001:DB8:4::/96 GE0/1/16 FE80::3A5D:67FF:FE41:305 20 A/-/-/- 2001:DB8:11::1/128 Loop1 Direct 0 D/-/L/- 2001:DB8:12::2/128 GE0/1/0 FE80::3A5D:67FF:FE31:307 10 A/-/-/- 2001:DB8:13::3/128 GE0/1/0 FE80::3A5D:67FF:FE31:307 20 A/-/-/- GE0/1/16 FE80::3A5D:67FF:FE41:305 2001:DB8:14::4/128 GE0/1/16 FE80::3A5D:67FF:FE41:305 10 A/-/-/- Flags: D-Direct, A-Added to URT, L-Advertised in LSPs, S-IGP Shortcut, U-Up/Down Bit Set, LP-Local Prefix-Sid Protect Type: L-Link Protect, N-Node Protect
- Configure delay attributes for Flex-Algo links.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] te attribute enable [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] te link-attribute-application flex-algo [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0-te-link-attribute-application] delay 10 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0-te-link-attribute-application] quit [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/16 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] te link-attribute-application flex-algo [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16-te-link-attribute-application] delay 20 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16-te-link-attribute-application] quit [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure P1.
[~P1] te attribute enable [*P1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] te link-attribute-application flex-algo [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0-te-link-attribute-application] delay 10 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0-te-link-attribute-application] quit [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] te link-attribute-application flex-algo [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8-te-link-attribute-application] delay 10 [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8-te-link-attribute-application] quit [*P1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] te attribute enable [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] te link-attribute-application flex-algo [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0-te-link-attribute-application] delay 10 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0-te-link-attribute-application] quit [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/16 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] te link-attribute-application flex-algo [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16-te-link-attribute-application] delay 20 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16-te-link-attribute-application] quit [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure P2.
[~P2] te attribute enable [*P2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] te link-attribute-application flex-algo [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0-te-link-attribute-application] delay 20 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0-te-link-attribute-application] quit [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] te link-attribute-application flex-algo [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8-te-link-attribute-application] delay 20 [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8-te-link-attribute-application] quit [*P2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*P2] commit
- Configure FADs.
You can select one or two devices in the same IGP domain to configure FADs. To improve reliability, you are advised to select two devices.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] flex-algo identifier 128 [*PE1-flex-algo-128] priority 100 [*PE1-flex-algo-128] metric-type delay [*PE1-flex-algo-128] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] flex-algo identifier 128 [*PE2-flex-algo-128] priority 100 [*PE2-flex-algo-128] metric-type delay [*PE2-flex-algo-128] quit [*PE2] commit
- Enable IS-IS-based Flex-Algo advertisement, IS-IS TE, and IS-IS-based IPv6 link delay advertisement.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] flex-algo 128 level-1 [*PE1-isis-1] ipv6 traffic-eng level-1 [*PE1-isis-1] ipv6 metric-delay advertisement enable level-1 [*PE1-isis-1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure P1.
[~P1] isis 1 [*P1-isis-1] flex-algo 128 level-1 [*P1-isis-1] ipv6 traffic-eng level-1 [*P1-isis-1] ipv6 metric-delay advertisement enable level-1 [*P1-isis-1] quit [*P1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] isis 1 [*PE2-isis-1] flex-algo 128 level-1 [*PE2-isis-1] ipv6 traffic-eng level-1 [*PE2-isis-1] ipv6 metric-delay advertisement enable level-1 [*PE2-isis-1] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure P2.
[~P2] isis 1 [*P2-isis-1] flex-algo 128 level-1 [*P2-isis-1] ipv6 traffic-eng level-1 [*P2-isis-1] ipv6 metric-delay advertisement enable level-1 [*P2-isis-1] quit [*P2] commit
- Configure a VPN instance on each PE, enable the IPv4 address family for the instance, and bind the interface that connects each PE to a CE to the VPN instance on that PE.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv4-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] vpn-target 111:1 both evpn [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.1.1.2 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv4-family [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 200:1 [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] vpn-target 111:1 both evpn [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.2.1.2 24 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE2] commit
# Assign an IP address to each interface on the CEs, as shown in Figure 1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
After the configuration is complete, run the display ip vpn-instance verbose command on the PEs to check VPN instance configurations. Check that each PE can successfully ping its connected CE.

If a PE has multiple interfaces bound to the same VPN instance, specify a source IP address using the -a source-ip-address parameter in the ping -vpn-instance vpn-instance-name -a source-ip-address dest-ip-address command to ping the CE that is connected to the remote PE. If the source IP address is not specified, the ping operation may fail.
- Establish an EBGP peer relationship between each PE and its connected CE.
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] interface loopback 1 [*CE1-LoopBack1] ip address 10.11.1.1 32 [*CE1-LoopBack1] quit [*CE1] bgp 65410 [*CE1-bgp] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 [*CE1-bgp] network 10.11.1.1 32 [*CE1-bgp] quit [*CE1] commit
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410 [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] import-route direct [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] commit [~PE1-bgp-vpn1] quit [~PE1-bgp] quit
# Configure CE2.
[~CE2] interface loopback 1 [*CE2-LoopBack1] ip address 10.22.2.2 32 [*CE2-LoopBack1] quit [*CE2] bgp 65420 [*CE2-bgp] peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 100 [*CE2-bgp] network 10.22.2.2 32 [*CE2-bgp] quit [*CE2] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 100 [*PE2-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*PE2-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE2-bgp-vpn1] peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65420 [*PE2-bgp-vpn1] import-route direct [*PE2-bgp-vpn1] commit [~PE2-bgp-vpn1] quit [~PE2-bgp] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display bgp vpnv4 vpn-instance peer command on the PEs to check whether BGP peer relationships have been established between the PEs and CEs. If the Established state is displayed in the command output, the BGP peer relationships have been established successfully.
The following example uses the command output on PE1 to show that a BGP peer relationship has been established between PE1 and CE1.
[~PE1] display bgp vpnv4 vpn-instance vpn1 peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 VPN-Instance vpn1, Router ID 1.1.1.1: Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 10.1.1.1 4 65410 310 318 0 04:26:42 Established 1 - Establish a BGP EVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [~PE1-bgp] peer 2001:db8:13::3 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 2001:db8:13::3 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE1-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 2001:db8:13::3 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] commit [~PE1-bgp-af-evpn] quit [~PE1-bgp] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 100 [~PE2-bgp] peer 2001:db8:11::1 as-number 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 2001:db8:11::1 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE2-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] peer 2001:db8:11::1 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] commit [~PE2-bgp-af-evpn] quit [~PE2-bgp] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display bgp evpn peer command on the PEs to check whether the BGP peer relationship has been established. If the Established state is displayed in the command output, the BGP peer relationship has been established successfully. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display bgp evpn peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 2001:DB8:13::3 4 100 314 311 0 04:27:06 Established 2
- Establish a Flex-Algo-based SRv6 BE path between the PEs.

An End.DT4 SID can be either dynamically allocated through BGP or manually configured. If a dynamically allocated SID and a manually configured SID both exist, the latter takes effect. If dynamic End.DT4 SID allocation through BGP has been enabled using the segment-routing ipv6 locator locator-name command, you do not need to run the opcode func-opcode end-dt4 vpn-instance vpn-instance-name command to configure a static SID opcode.
In this example, SIDs are dynamically allocated through BGP.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] segment-routing ipv6 [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2001:db8:11::1 [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator PE1 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:100:: 64 static 32 flex-algo 128 [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator] quit [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit [*PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 2001:db8:13::3 advertise encap-type srv6 [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] advertise l2vpn evpn [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator PE1 evpn [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator PE1 [*PE1-isis-1] commit [~PE1-isis-1] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] segment-routing ipv6 [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2001:db8:13::3 [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator PE2 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:300:: 64 static 32 flex-algo 128 [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator] quit [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit [*PE2] bgp 100 [*PE2-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] peer 2001:db8:11::1 advertise encap-type srv6 [*PE2-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE2-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE2-bgp-vpn1] advertise l2vpn evpn [*PE2-bgp-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn [*PE2-bgp-vpn1] segment-routing ipv6 locator PE2 evpn [*PE2-bgp-vpn1] quit [*PE2-bgp] quit [*PE2] isis 1 [*PE2-isis-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator PE2 [*PE2-isis-1] commit [~PE2-isis-1] quit
# Configure P1.
[~P1] segment-routing ipv6 [*P1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator P1 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:200:: 64 static 32 flex-algo 128 [*P1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator] quit [*P1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit [*P1] isis 1 [*P1-isis-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator P1 [*P1-isis-1] commit [~P1-isis-1] quit
# Configure P2.
[~P2] segment-routing ipv6 [*P2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator P2 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:400:: 64 static 32 flex-algo 128 [*P2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator] quit [*P2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit [*P2] isis 1 [*P2-isis-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator P2 [*P2-isis-1] commit [~P2-isis-1] quit
- Verify the configuration.
Run the display segment-routing ipv6 locator [ locator-name ] verbose command to check SRv6 locator information. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display segment-routing ipv6 locator verbose Locator Configuration Table --------------------------- LocatorName : PE1 LocatorID : 3 IPv6Prefix : 2001:DB8:100:: PrefixLength : 64 Block : -- BlockLength : 0 NodeID : -- NodeIdLength : 0 ComprStaticLen: 0 StaticLength : 32 ArgsLength : 0 Reference : 0 AutoCSIDPoolID: 0 ComprDynLength: 0 Algorithm : 128 AutoCSIDBegin : -- AutoCSIDEnd : -- StaticCSIDBegin: -- StaticCSIDEnd : -- AutoSIDPoolID : 8194 DynLength : 32 AutoSIDBegin : 2001:DB8:100::1:0:0 AutoSIDEnd : 2001:DB8:100:0:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF StaticSIDBegin: 2001:DB8:100::1 StaticSIDEnd : 2001:DB8:100::FFFF:FFFF Total Locator(s): 1Run the display segment-routing ipv6 local-sid end-dt4 forwarding command to check information about the SRv6 local SID table. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display segment-routing ipv6 local-sid end-dt4 forwarding My Local-SID End.DT4 Forwarding Table ------------------------------------- SID : 2001:DB8:100::1:0:3C/128 FuncType : End.DT4 VPN Name : vpn1 VPN ID : 3 LocatorName: PE1 LocatorID: 1 Total SID(s): 1Run the display isis route ipv6 flex-algo 128 command on the PEs to check routing information about IS-IS Flex-Algo 128. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display isis route ipv6 flex-algo 128 Route information for ISIS(1) ----------------------------- ISIS(1) Level-1 Flex-Algo Forwarding Table ------------------------------------------ IPV6 Dest. ExitInterface NextHop Cost Flags -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2001:DB8:100::/64 NULL0 - 0 A/-/-/- 2001:DB8:200::/64 GE0/1/0 FE80::3A5D:67FF:FE31:307 10 A/-/-/- 2001:DB8:300::/64 GE0/1/0 FE80::3A5D:67FF:FE31:307 20 A/-/-/- 2001:DB8:400::/64 GE0/1/16 FE80::3A5D:67FF:FE41:305 20 A/-/-/- Flags: D-Direct, A-Added to URT, L-Advertised in LSPs, S-IGP Shortcut, U-Up/Down Bit Set, LP-Local Prefix-Sid Protect Type: L-Link Protect, N-Node ProtectThe command output shows that the outbound interface of the locator route 2001:DB8:300::/64 is GE 0/1/0, indicating that data traffic is forwarded along the PE1-P1-PE2 link with a low delay.
Run the display bgp evpn all routing-table command on the PEs to check BGP EVPN routing information. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display bgp evpn all routing-table Local AS number : 100 BGP Local router ID is 1.1.1.1 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete EVPN address family: Number of Ip Prefix Routes: 4 Route Distinguisher: 100:1 Network(EthTagId/IpPrefix/IpPrefixLen) NextHop *> 0:10.1.1.0:24 0.0.0.0 *> 0:10.11.1.1:32 10.1.1.1 Route Distinguisher: 200:1 Network(EthTagId/IpPrefix/IpPrefixLen) NextHop *>i 0:10.2.1.0:24 2001:DB8:13::3 *>i 0:10.22.2.2:32 2001:DB8:13::3 [~PE1] display bgp evpn all routing-table prefix-route 0:10.22.2.2:32 BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total routes of Route Distinguisher(200:1): 1 BGP routing table entry information of 0:10.22.2.2:32: Label information (Received/Applied): 3/NULL From: 2001:DB8:13::3 (2.2.2.2) Route Duration: 0d04h42m41s Relay IP Nexthop: FE80::3A5D:67FF:FE31:307 Relay IP Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Relay Tunnel Out-Interface: Original nexthop: 2001:DB8:13::3 Qos information : 0x0 Ext-Community: RT <111 : 1> Prefix-sid: 2001:DB8:300::1:0:3E AS-path 65420, origin igp, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, best, select, pre 255, IGP cost 20 Route Type: 5 (Ip Prefix Route) Ethernet Tag ID: 0, IP Prefix/Len: 10.22.2.2/32, ESI: 0000.0000.0000.0000.0000, GW IP Address: 0.0.0.0 Not advertised to any peer yetRun the display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 command on the PEs to check routing table information about the specified VPN instance. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : vpn1 Destinations : 8 Routes : 8 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.2.1.0/24 IBGP 255 0 RD 2001:DB8:300::1:0:3E SRv6 BE 10.11.1.1/32 EBGP 255 0 RD 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.22.2.2/32 IBGP 255 0 RD 2001:DB8:300::1:0:3E SRv6 BE 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0Run the display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 ip-address verbose command on the PEs to check detailed routing table information about the specified VPN instance. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 10.22.2.2 verbose Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : vpn1 Summary Count : 1 Destination: 10.22.2.2/32 Protocol: IBGP Process ID: 0 Preference: 255 Cost: 0 NextHop: 2001:DB8:300::1:0:3E Neighbour: 2001:DB8:13::3 State: Active Adv Relied Age: 03h36m34s Tag: 0 Priority: low Label: NULL QoSInfo: 0x0 IndirectID: 0x10000E3 Instance: RelayNextHop: 2001:DB8:300::1:0:3E Interface: SRv6 BE TunnelID: 0x0 Flags: RDCheck that CEs belonging to the same VPN instance can ping each other. The following example uses the command output on CE1.
[~CE1] ping -a 10.11.1.1 10.22.2.2 PING 10.22.2.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 10.22.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=253 time=3 ms Reply from 10.22.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=253 time=3 ms Reply from 10.22.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=253 time=3 ms Reply from 10.22.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=253 time=3 ms Reply from 10.22.2.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=253 time=3 ms --- 10.22.2.2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 3/3/3 ms
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity evpn vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity evpn # te attribute enable # flex-algo identifier 128 priority 100 metric-type delay # segment-routing ipv6 encapsulation source-address 2001:db8:11::1 locator PE1 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:100:: 64 static 32 flex-algo 128 # isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 flex-algo 128 level-1 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 ipv6 traffic-eng level-1 ipv6 metric-delay advertisement enable level-1 segment-routing ipv6 locator PE1 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::1/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 te link-attribute-application flex-algo delay 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:3::1/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 te link-attribute-application flex-algo delay 20 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:11::1/128 isis ipv6 enable 1 # bgp 100 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 2001:db8:13::3 as-number 100 peer 2001:db8:13::3 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 import-route direct advertise l2vpn evpn segment-routing ipv6 locator PE1 evpn segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410 # l2vpn-family evpn policy vpn-target peer 2001:db8:13::3 enable peer 2001:db8:13::3 advertise encap-type srv6 # return
P1 configuration file
# sysname P1 # te attribute enable # segment-routing ipv6 locator P1 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:200:: 64 static 32 flex-algo 128 # isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 flex-algo 128 level-1 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 ipv6 traffic-eng level-1 ipv6 metric-delay advertisement enable level-1 segment-routing ipv6 locator P1 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::2/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 te link-attribute-application flex-algo delay 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::1/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 te link-attribute-application flex-algo delay 10 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:12::2/128 isis ipv6 enable 1 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 200:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity evpn vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity evpn # te attribute enable # flex-algo identifier 128 priority 100 metric-type delay # segment-routing ipv6 encapsulation source-address 2001:db8:13::3 locator PE2 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:300:: 64 static 32 flex-algo 128 # isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 flex-algo 128 level-1 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 ipv6 traffic-eng level-1 ipv6 metric-delay advertisement enable level-1 segment-routing ipv6 locator PE2 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::2/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 te link-attribute-application flex-algo delay 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:4::2/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 te link-attribute-application flex-algo delay 10 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:13::3/128 isis ipv6 enable 1 # bgp 100 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 2001:db8:11::1 as-number 100 peer 2001:db8:11::1 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 import-route direct advertise l2vpn evpn segment-routing ipv6 locator PE2 evpn segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65420 # l2vpn-family evpn policy vpn-target peer 2001:db8:11::1 enable peer 2001:db8:11::1 advertise encap-type srv6 # return
P2 configuration file
# sysname P2 # te attribute enable # segment-routing ipv6 locator P2 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:400:: 64 static 32 flex-algo 128 # isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 flex-algo 128 level-1 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 ipv6 traffic-eng level-1 ipv6 metric-delay advertisement enable level-1 segment-routing ipv6 locator P2 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:3::2/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 te link-attribute-application flex-algo delay 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:4::1/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 te link-attribute-application flex-algo delay 20 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:14::4/128 isis ipv6 enable 1 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 10.11.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65410 peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 network 10.11.1.1 255.255.255.255 # ipv4-family unicast peer 10.1.1.2 enable # returnCE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 10.22.2.2 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65420 peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 100 network 10.22.2.2 255.255.255.255 # ipv4-family unicast peer 10.2.1.2 enable # return