Example for Configuring Inter-AS L3VPNv4 over SRv6 BE
This section provides an example for configuring an inter-AS SRv6 BE path to carry L3VPNv4 services.
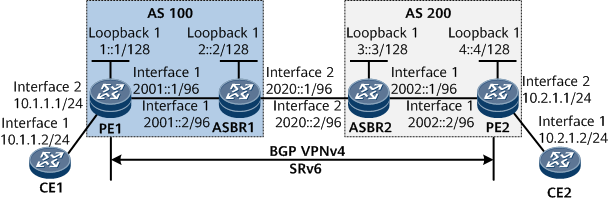
Networking Requirements
PE1 and ASBR1 belong to AS 100, and PE2 and ASBR2 belong to AS 200. Intra-AS IPv6 connectivity needs to be achieved for AS 100 and AS 200 through IS-IS.
PE1 and ASBR1 belong to IS-IS process 1, and PE2 and ASBR2 belong to IS-IS process 10. PE1, ASBR1, PE2, and ASBR2 are all Level-1 devices.
It is required that a bidirectional inter-AS SRv6 BE path be deployed between PE1 and PE2 to carry L3VPNv4 services.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure an IPv6 address for each interface on the PEs and ASBRs.
Enable IS-IS, configure an IS-IS level, and specify a network entity title (NET) on each PE and ASBR.
Configure VPN instances on PE1 and PE2.
Establish an EBGP peer relationship between each PE and its connected CE.
- Enable IS-IS SRv6 on each PE and ASBR.
- Configure locator route import between the ASBRs.
Establish an MP-EBGP peer relationship between the PEs.
- Configure the PEs to exchange BGP VPNv4 routes carrying SIDs through this peer relationship.
Configure SRv6 forwarding on the PEs.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Interface IPv6 addresses on each device
AS numbers of the PEs and ASBRs
IS-IS process IDs, levels, and NETs of the PEs and ASBRs
VPN instance name, RD, and RT on PE1 and PE2
Procedure
- Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure an IPv6 address for each interface. The following example uses the configuration of PE1. The configurations of other devices are similar to the configuration of PE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ipv6 enable [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ipv6 address 2001::1 96 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] interface loopback1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 enable [*PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1::1 128 [*PE1-LoopBack1] commit [~PE1-LoopBack1] quit
- Configure IS-IS.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1 [*PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide [*PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 [*PE1-isis-1] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*PE1-isis-1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE1] interface loopback1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] commit [~PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure ASBR1.
[~ASBR1] isis 1 [*ASBR1-isis-1] is-level level-1 [*ASBR1-isis-1] cost-style wide [*ASBR1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 [*ASBR1-isis-1] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*ASBR1-isis-1] quit [*ASBR1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*ASBR1] interface loopback1 [*ASBR1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1 [*ASBR1-LoopBack1] commit [~ASBR1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure ASBR2.
[~ASBR2] isis 10 [*ASBR2-isis-10] is-level level-1 [*ASBR2-isis-10] cost-style wide [*ASBR2-isis-10] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 [*ASBR2-isis-10] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*ASBR2-isis-10] quit [*ASBR2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 10 [*ASBR2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*ASBR2] interface loopback1 [*ASBR2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 10 [*ASBR2-LoopBack1] commit [~ASBR2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] isis 10 [*PE2-isis-10] is-level level-1 [*PE2-isis-10] cost-style wide [*PE2-isis-10] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 [*PE2-isis-10] ipv6 enable topology ipv6 [*PE2-isis-10] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] isis ipv6 enable 10 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE2] interface loopback1 [*PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 10 [*PE2-LoopBack1] commit [~PE2-LoopBack1] quit
After the configuration is complete, perform the following operations to check whether IS-IS is successfully configured:
# Display IS-IS neighbor information. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display isis peer Peer information for ISIS(1) System Id Interface Circuit Id State HoldTime Type PRI -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0000.0000.0002* GE0/1/0 0000.0000.0002.01 Up 8s L1 64 Total Peer(s): 1
- Configure a VPN instance on each PE, enable the IPv4 address family for the instance, and bind the interface that connects a PE to a CE to the VPN instance on that PE.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] ip vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv4-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] vpn-target 111:1 both [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] ip vpn-instance vpna [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv4-family [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 200:1 [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] vpn-target 111:1 both [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.2.1.1 24 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE2] commit
# Assign an IP address to each interface on the CEs, as shown in Figure 1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
After the configuration is complete, run the display ip vpn-instance verbose command on the PEs to check VPN instance configurations. The command output shows that each PE can successfully ping its connected CE.

If a PE has multiple interfaces bound to the same VPN instance, specify a source IP address using the -a source-ip-address parameter in the ping -vpn-instance vpn-instance-name -a source-ip-address dest-ip-address command to ping the CE that is connected to the remote PE. If the source IP address is not specified, the ping operation may fail.
- Establish an EBGP peer relationship between each PE and its connected CE.
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] interface loopback 1 [*CE1-LoopBack1] ip address 11.11.11.11 32 [*CE1-LoopBack1] quit [*CE1] bgp 65410 [*CE1-bgp] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 100 [*CE1-bgp] network 11.11.11.11 32 [*CE1-bgp] quit [*CE1] commit
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-bgp-vpna] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 65410 [*PE1-bgp-vpna] import-route direct [*PE1-bgp-vpna] commit [~PE1-bgp-vpna] quit [~PE1-bgp] quit
# Configure CE2.
[~CE2] interface loopback 1 [*CE2-LoopBack1] ip address 22.22.22.22 32 [*CE2-LoopBack1] quit [*CE2] bgp 65420 [*CE2-bgp] peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 200 [*CE2-bgp] network 22.22.22.22 32 [*CE2-bgp] quit [*CE2] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 200 [*PE2-bgp] router-id 4.4.4.4 [*PE2-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE2-bgp-vpna] peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 65420 [*PE2-bgp-vpna] import-route direct [*PE2-bgp-vpna] commit [~PE2-bgp-vpna] quit [~PE2-bgp] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display bgp vpnv4 vpn-instance peer command on the PEs to check whether BGP peer relationships have been established between the PEs and CEs. If the Established state is displayed in the command output, the BGP peer relationships have been established successfully.
The following example uses the command output on PE1 to show that a BGP peer relationship has been established between PE1 and CE1.
[~PE1] display bgp vpnv4 vpn-instance vpna peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 VPN-Instance vpna, Router ID 1.1.1.1: Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 10.1.1.2 4 65410 11 9 0 00:06:37 Established 1 - Configure IS-IS on the PEs to advertise SRv6 locator routes.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] segment-routing ipv6 [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1 [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator as1 ipv6-prefix 10:: 64 static 32 [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator] quit [*PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit [*PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 [*PE1-isis-1] commit [~PE1-isis-1] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] segment-routing ipv6 [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4 [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator as1 ipv6-prefix 40:: 64 static 32 [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator] quit [*PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit [*PE2] isis 10 [*PE2-isis-10] segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 [*PE2-isis-10] commit [~PE2-isis-10] quit
- Configure locator route import.
Configure locator route import in the PE1 -> PE2 direction. Specifically, configure BGP on ASBR1 to import the locator routes advertised by PE1 through IS-IS and advertise the routes to ASBR2. In addition, configure IS-IS on ASBR2 to import BGP routes, thereby also advertising the locator routes of PE1 to PE2 through IS-IS. Then, configure locator route import in the PE2 -> PE1 direction in a similar way.
# Configure ASBR1.
[~ASBR1] bgp 100 [*ASBR1-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*ASBR1-bgp] peer 2020::2 as-number 200 [*ASBR1-bgp] peer 2020::2 ebgp-max-hop 255 [*ASBR1-bgp] ipv6-family unicast [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 2020::2 enable [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv6] network 10:: 64 [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv6] network 1::1 128 [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv6] quit [*ASBR1-bgp] quit [*ASBR1] ip ipv6-prefix p1 permit 40:: 64 [*ASBR1] ip ipv6-prefix p1 permit 4::4 128 [*ASBR1] route-policy rp1 permit node 10 [*ASBR1-route-policy] if-match ipv6 address prefix-list p1 [*ASBR1-route-policy] quit [*ASBR1] isis 1 [*ASBR1-isis-1] ipv6 import-route bgp route-policy rp1 level-1 [*ASBR1-isis-1] quit [*ASBR1] commit
# Configure ASBR2.
[~ASBR2] bgp 200 [*ASBR2-bgp] router-id 3.3.3.3 [*ASBR2-bgp] peer 2020::1 as-number 100 [*ASBR2-bgp] peer 2020::1 ebgp-max-hop 255 [*ASBR2-bgp] ipv6-family unicast [*ASBR2-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 2020::1 enable [*ASBR2-bgp-af-ipv6] network 40:: 64 [*ASBR2-bgp-af-ipv6] network 4::4 128 [*ASBR2-bgp-af-ipv6] quit [*ASBR2-bgp] quit [*ASBR2] ip ipv6-prefix p1 permit 10:: 64 [*ASBR2] ip ipv6-prefix p1 permit 1::1 128 [*ASBR2] route-policy rp1 permit node 10 [*ASBR2-route-policy] if-match ipv6 address prefix-list p1 [*ASBR2-route-policy] quit [*ASBR2] isis 10 [*ASBR2-isis-10] ipv6 import-route bgp route-policy rp1 level-1 [*ASBR2-isis-10] quit [*ASBR2] commit
- Establish an MP-EBGP peer relationship between the PEs, configure the PEs to exchange BGP VPNv4 routes carrying SIDs through this peer relationship, and enable SRv6 BE forwarding on the PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [~PE1-bgp] peer 4::4 as-number 200 [*PE1-bgp] peer 4::4 ebgp-max-hop 255 [*PE1-bgp] peer 4::4 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 4::4 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 4::4 prefix-sid [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE1-bgp-vpna] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort [*PE1-bgp-vpna] segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 [*PE1-bgp-vpna] commit [~PE1-bgp-vpna] quit [~PE1-bgp] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 200 [~PE2-bgp] peer 1::1 as-number 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 255 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE2-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [*PE2-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE2-bgp-vpna] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort [*PE2-bgp-vpna] segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 [*PE2-bgp-vpna] commit [~PE2-bgp-vpna] quit [~PE2-bgp] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display bgp vpnv4 all peer command on the PEs to check whether BGP peer relationships have been established between the PEs. If the Established state is displayed in the command output, the BGP peer relationships have been established successfully. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display bgp vpnv4 all peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 2 Peers in established state : 2 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 4::4 4 200 1512 1520 0 21:55:19 Established 2 Peer of IPv4-family for vpn instance : VPN-Instance vpna, Router ID 1.1.1.1: Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 10.1.1.2 4 65410 1790 1812 0 0026h03m Established 1
- Verify the configuration.
Run the display segment-routing ipv6 locator [ locator-name ] verbose command to check SRv6 locator information. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display segment-routing ipv6 locator verbose Locator Configuration Table --------------------------- LocatorName : as1 LocatorID : 4 IPv6Prefix : 10:: PrefixLength : 64 Block : -- BlockLength : 0 NodeID : -- NodeIdLength : 0 ComprStaticLen: 0 StaticLength : 32 ArgsLength : 0 Reference : 0 AutoCSIDPoolID: 0 ComprDynLength: 0 AutoCSIDBegin : -- AutoCSIDEnd : -- StaticCSIDBegin: -- StaticCSIDEnd : -- AutoSIDPoolID : 8195 DynLength : 32 AutoSIDBegin : 10::1:0:0 AutoSIDEnd : 10::FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF StaticSIDBegin: 10::1 StaticSIDEnd : 10::FFFF:FFFF Total Locator(s): 1Run the display segment-routing ipv6 local-sid end-dt4 forwarding command to check information about the SRv6 local SID table. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display segment-routing ipv6 local-sid end-dt4 forwarding My Local-SID End.DT4 Forwarding Table ------------------------------------- SID : 10::1:0:20/128 FuncType : End.DT4 VPN Name : vpna VPN ID : 3 LocatorName: as1 LocatorID: 1 Total SID(s): 1Run the ping command on a CE. The command output shows that CEs belonging to the same VPN can ping each other. For example:
[~CE1] ping -a 11.11.11.11 22.22.22.22 PING 22.22.22.22: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 22.22.22.22: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=253 time=22 ms Reply from 22.22.22.22: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=253 time=13 ms Reply from 22.22.22.22: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=253 time=14 ms Reply from 22.22.22.22: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=253 time=15 ms Reply from 22.22.22.22: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=253 time=34 ms --- 22.22.22.22 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 13/19/34 ms
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity # segment-routing ipv6 encapsulation source-address 1::1 locator as1 ipv6-prefix 10:: 64 static 32 # isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001::1/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 1::1/128 isis ipv6 enable 1 # bgp 100 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 4::4 as-number 200 peer 4::4 ebgp-max-hop 255 peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 4::4 enable peer 4::4 prefix-sid # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna import-route direct segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 segment-routing ipv6 best-effort peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 65410 # return
ASBR1 configuration file
# sysname ASBR1 # isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 ipv6 import-route bgp route-policy rp1 level-1 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001::2/96 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2020::1/96 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2::2/128 isis ipv6 enable 1 # bgp 100 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 2020::2 as-number 200 peer 2020::2 ebgp-max-hop 255 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization network 10:: 64 network 1::1 128 peer 2020::2 enable # route-policy rp1 permit node 10 if-match ipv6 address prefix-list p1 # ip ipv6-prefix p1 index 10 permit 40:: 64 ip ipv6-prefix p1 index 20 permit 4::4 128 # return
ASBR2 configuration file
# sysname ASBR2 # isis 10 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 ipv6 import-route bgp route-policy rp1 level-1 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2002::1/96 isis ipv6 enable 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2020::2/96 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 3::3/128 isis ipv6 enable 10 # bgp 200 router-id 3.3.3.3 peer 2020::1 as-number 100 peer 2020::1 ebgp-max-hop 255 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization network 40:: 64 network 4::4 128 peer 2020::1 enable # route-policy rp1 permit node 10 if-match ipv6 address prefix-list p1 # ip ipv6-prefix p1 index 10 permit 10:: 64 ip ipv6-prefix p1 index 20 permit 1::1 128 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 200:1 vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity # segment-routing ipv6 encapsulation source-address 4::4 locator as1 ipv6-prefix 40:: 64 static 32 # isis 10 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 # ipv6 enable topology ipv6 segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2002::2/96 isis ipv6 enable 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 4::4/128 isis ipv6 enable 10 # bgp 200 router-id 4.4.4.4 peer 1::1 as-number 100 peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 255 peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 1::1 enable peer 1::1 prefix-sid # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna import-route direct segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 segment-routing ipv6 best-effort peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 65420 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65410 peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255 peer 10.1.1.1 enable # returnCE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 22.22.22.22 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65420 peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 22.22.22.22 255.255.255.255 peer 10.2.1.1 enable # return