Configuring an RSVP Authentication Mode
RSVP authentication modes are configured between RSVP neighboring nodes or between the interfaces of RSVP neighboring nodes. The keys on both ends to be authenticated must be the same; otherwise, RSVP authentication fails, and RSVP neighboring nodes discard received packets.
Context
RSVP authentication in the key mode is used to prevent an unauthorized node from establishing an RSVP neighbor relationship with a local node. It can also prevent a remote node from constructing forged packets to establish an RSVP neighbor relationship with the local node.
Local interface-based authentication
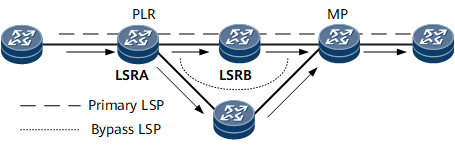
Local interface-based authentication is performed between interfaces connecting a point of local Repair (PLR) and a merge point (MP) in an inter-domain MPLS TE FRR scenario.
- Local interface-based authentication is recommended on a network configured with inter-domain MPLS TE FRR.
- Local interface- or neighbor interface-based authentication can be used on a network that is not configured with inter-domain MPLS TE FRR.
Neighbor node-based authentication
Neighbor node-based authentication takes effect on an entire device. It is usually performed between a PLR and an MP based on LSR IDs.
This authentication mode is recommended on a network with non-inter-domain MPLS TE FRR.
Neighbor interface-based authentication
Neighbor interface-based authentication is performed between interfaces connecting two LSRs. For example, neighbor interface-based authentication is performed between interfaces connecting LSRA and LSRB shown in the Figure 1.
Local interface- or neighbor interface-based authentication can be used on a network that is not configured with inter-domain MPLS TE FRR.
Each pair of RSVP neighbors must use the same key; otherwise, RSVP authentication fails, and all received RSVP messages are discarded.
Table1 Rules for RSVP authentication mode selection describes differences between local interface-, neighbor node-, and neighbor address-based authentication modes.
RSVP Key Authentication |
Local Interface-based Authentication |
Neighbor Node-based Authentication |
Neighbor Interface-based Authentication |
|---|---|---|---|
Authentication mode |
Local interface-based authentication |
RSVP neighbor-based authentication |
RSVP neighbor interface-based authentication |
Priority |
High |
Medium |
Low |
Applicable environment |
Any network |
Non-inter-area network |
Networks on which MPLS TE FRR is enabled and primary CR-LSPs are in the FRR Inuse state |
Advantages |
N/A |
Simplex configuration |
N/A |