Configuring Leaf Lists
Configuring a leaf list on an ingress specifies all leaf nodes on a P2MP TE tunnel. A leaf list helps you configure and manage these leaf nodes uniformly. The steps in this section must be performed if P2MP TE tunnels are manually established. The steps in this section are optional if the establishment of P2MP TE tunnels is automatically triggered by a service.
Context
For a P2MP TE tunnel, the path that originates from the ingress and is destined for each leaf node can be calculated either by constraint shortest path first (CSPF) or by planning an explicit path for a specific leaf node or each leaf node. After each leaf node is configured on an ingress, the ingress sends signaling packets to each leaf node and then establishes a P2MP TE tunnel. The NetEngine 8000 F uses leaf lists to configure and manage leaf nodes. All leaf nodes and their explicit paths are integrated into a table, which helps you configure and manage the leaf nodes uniformly.
An MPLS network that transmits multicast services selects dynamically leaf nodes on an automatic P2MP TE tunnel and uses constrained shortest path first (CSPF) to calculate a path destined for each leaf node. To control the leaf nodes of an automatic P2MP TE tunnel, configure a leaf list.
Explicit path planning requires you to configure an explicit path for a specific leaf node or each leaf node, and use the explicit path in the leaf list view.

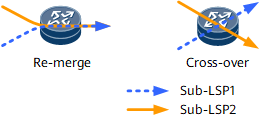
- Remerge event: occurs when two sub-LSPs have different inbound interfaces but the same outbound interface on a transit node. Figure 1 shows that a remerge event occurs on the outbound interface shared by two sub-LSPs.
- Crossover event: occurs when two sub-LSPs have different inbound and outbound interfaces on a transit node. Figure 1 shows that a crossover event occurs on the transit node shared by the two sub-LSPs.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- (Optional) Configure an explicit path to each leaf node.
For a P2MP TE tunnel, an explicit tunnel can be configured for a specific leaf node or each leaf node.
- Run mpls te leaf-list leaf-list-name
A leaf list is established for a P2MP RSVP-TE tunnel.
- Run destination leaf-address
A leaf node is established in the leaf list.
The leaf-address parameter specifies the MPLS LSR ID of each leaf node.
- (Optional) Run path explicit-path path-name
An explicit path is specified for the leaf node.
The explicit-path path-name parameter specifies the name of the explicit path established in Step 2.

Repeat Step 3 and Step 4 on a P2MP TE tunnel to configure all leaf nodes.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.