Configuring P2MP TE FRR
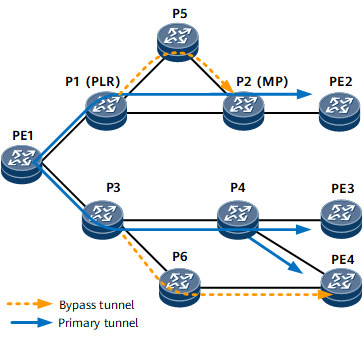
P2MP TE fast reroute (FRR) provides local link protection for a P2MP TE tunnel. It establishes a bypass tunnel to protect sub-LSPs. If a link fails on the P2MP TE tunnel, traffic switches to the bypass tunnel within 50 milliseconds, which increases tunnel reliability.
Usage Scenario
P2MP TE FRR establishes a bypass tunnel to provide local link protection for the P2MP TE tunnel called the primary tunnel. The bypass tunnel is a P2P TE tunnel. The principles and concepts of P2MP TE FRR are similar to those of P2P TE FRR.
P2P and P2MP TE tunnels can share a bypass tunnel. Therefore, when planning bandwidth for the bypass tunnel, ensure that the bypass tunnel bandwidth is equal to the total bandwidth of the bound P2P and P2MP tunnels.

If traffic is switched to a P2MP FRR tunnel, the forwarding performance deteriorates temporarily, and the impact is removed after traffic switches back to the primary tunnel.
In NG MVPN scenarios, when P2MP TE FRR protection is used, the interface of a primary P2MP tunnel needs to be enabled to delay in going Up. The delay is related to the number of VPN multicast groups over the tunnel. For 1000 multicast groups, set the delay time to 30s. Increase the delay time if more multicast groups are configured.
- Configuring Manual FRR for a Manually Configured P2MP TE Tunnel
- Manual FRR can be configured on the tunnel interface of a manually configured P2MP TE tunnel.
- Configuring FRR for Automatic P2MP TE Tunnels
- Auto P2MP TE FRR is configured in a P2MP TE template for automatic P2MP TE tunnels.
- Verifying the P2MP TE FRR Configuration
- After configuring P2MP TE FRR, verify P2MP TE FRR information.