Example for Configuring a 1:1 Tunnel Protection Group Consisting of Bidirectional Co-routed CR-LSPs
This section provides an example for configuring a 1:1 tunnel protection group consisting of static bidirectional co-routed CR-LSPs. A tunnel protection group provides end-to-end protection for MPLS TE traffic if a network fault occurs.
Context
A tunnel protection group consists of static bidirectional co-routed CR-LSPs. If the working tunnel fails, traffic is switched to the protection tunnel, which helps improve network reliability.
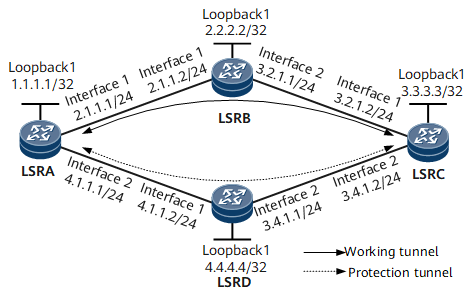
On the MPLS network shown in Figure 1, a working tunnel is established over the path LSRA -> LSRB -> LSRC, and a protection tunnel is established over the path LSRA -> LSRD -> LSRC. To ensure that MPLS TE traffic is not interrupted if a fault occurs, configure static bidirectional co-routed CR-LSPs for both the working and protection tunnels and combine them into a tunnel protection group.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Assign an IP address to each interface and configure a routing protocol.
Configure basic MPLS functions and enable MPLS TE.
Configure the ingress, transit nodes, and egress for each static bidirectional co-routed CR-LSP.
Configure MPLS TE tunnel interfaces for the working and protection tunnels and bind a specific static bidirectional co-routed CR-LSP to each tunnel interface.
Configure a tunnel protection group.
Configure a detection mechanism to monitor the configured tunnel protection group. MPLS-TP OAM is used in this example.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Tunnel interface names, tunnel interface IP addresses, destination addresses, tunnel IDs, and tunnel signaling protocol (CR-Static) on LSRA and LSRC
Next-hop address and outgoing label on the ingress
Inbound interface name, next-hop address, and outgoing label on the transit node
Inbound interface name on the egress
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface and configure a routing protocol.
# Assign an IP address and a mask to each interface and configure static routes so that all LSRs can interconnect with each other.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure basic MPLS functions and enable MPLS TE.
# Configure LSRA.
[~LSRA] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [*LSRA] mpls [*LSRA-mpls] mpls te [*LSRA-mpls] quit [*LSRA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls te [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*LSRA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls te [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
Repeat this step for LSRB, LSRC, and LSRD. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure the ingress, transit nodes, and egress for each static bidirectional co-routed CR-LSP.# Configure LSRA as the ingress on both the working and protection static bidirectional co-routed CR-LSPs.
[~LSRA] bidirectional static-cr-lsp ingress Tunnel10 [*LSRA-bi-static-ingress-Tunnel10] forward nexthop 2.1.1.2 out-label 20 [*LSRA-bi-static-ingress-Tunnel10] backward in-label 20 [*LSRA-bi-static-ingress-Tunnel10] quit [*LSRA] bidirectional static-cr-lsp ingress Tunnel11 [*LSRA-bi-static-ingress-Tunnel11] forward nexthop 4.1.1.2 out-label 21 [*LSRA-bi-static-ingress-Tunnel11] backward in-label 21 [*LSRA-bi-static-ingress-Tunnel11] commit [~LSRA-bi-static-ingress-Tunnel11] quit
# Configure LSRB as a transit node on the working static bidirectional co-routed CR-LSP.[~LSRB]bidirectional static-cr-lsp transit lsp1 [*LSRB-bi-static-transit-lsp1] forward in-label 20 nexthop 3.2.1.2 out-label 40 [*LSRB-bi-static-transit-lsp1] backward in-label 16 nexthop 2.1.1.1 out-label 20 [*LSRB-bi-static-transit-lsp1] commit [~LSRB-bi-static-transit-lsp1] quit
# Configure LSRD as a transit node on the protection static bidirectional co-routed CR-LSP.[~LSRD]bidirectional static-cr-lsp transit lsp2 [*LSRD-bi-static-transit-lsp2] forward in-label 21 nexthop 3.4.1.2 out-label 41 [*LSRD-bi-static-transit-lsp2] backward in-label 17 nexthop 4.1.1.1 out-label 21 [*LSRD-bi-static-transit-lsp2] commit [~LSRD-bi-static-transit-lsp2] quit
# Configure LSRC as the egress on both the working and protection static bidirectional co-routed CR-LSPs.[~LSRC] bidirectional static-cr-lsp egress lsp1 [*LSRC-bi-static-egress-lsp1] forward in-label 40 lsrid 1.1.1.1 tunnel-id 100 [*LSRC-bi-static-egress-lsp1] backward nexthop 3.2.1.1 out-label 16 [*LSRC-bi-static-egress-lsp1] quit [*LSRC] bidirectional static-cr-lsp egress lsp2 [*LSRC-bi-static-egress-lsp2] forward in-label 41 lsrid 1.1.1.1 tunnel-id 101 [*LSRC-bi-static-egress-lsp2] backward nexthop 3.4.1.1 out-label 17 [*LSRC-bi-static-egress-lsp2] commit [~LSRC-bi-static-egress-lsp2] quit
- Configure MPLS TE tunnel interfaces for the working and protection tunnels and bind a specific static bidirectional co-routed CR-LSP to each tunnel interface.
# On LSRA, configure MPLS TE tunnel interfaces named Tunnel 10 and Tunnel 11.
[~LSRA] interface Tunnel 10 [*LSRA-Tunnel10] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 1 [*LSRA-Tunnel10] tunnel-protocol mpls te [*LSRA-Tunnel10] destination 3.3.3.3 [*LSRA-Tunnel10] mpls te tunnel-id 100 [*LSRA-Tunnel10] mpls te signal-protocol cr-static [*LSRA-Tunnel10] mpls te bidirectional [*LSRA-Tunnel10] quit [*LSRA] interface Tunnel 11 [*LSRA-Tunnel11] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 1 [*LSRA-Tunnel11] tunnel-protocol mpls te [*LSRA-Tunnel11] destination 3.3.3.3 [*LSRA-Tunnel11] mpls te tunnel-id 101 [*LSRA-Tunnel11] mpls te signal-protocol cr-static [*LSRA-Tunnel11] mpls te bidirectional [*LSRA-Tunnel11] commit [~LSRA-Tunnel11] quit
# On LSRC, configure MPLS TE tunnel interfaces named Tunnel 20 and Tunnel 21.
[~LSRC] interface Tunnel 20 [*LSRC-Tunnel20] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 1 [*LSRC-Tunnel20] tunnel-protocol mpls te [*LSRC-Tunnel20] destination 1.1.1.1 [*LSRC-Tunnel20] mpls te tunnel-id 200 [*LSRC-Tunnel20] mpls te signal-protocol cr-static [*LSRC-Tunnel20] mpls te passive-tunnel [*LSRC-Tunnel20] mpls te binding bidirectional static-cr-lsp egress lsp1 [*LSRC-Tunnel20] quit [*LSRC] interface Tunnel 21 [*LSRC-Tunnel21] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 1 [*LSRC-Tunnel21] tunnel-protocol mpls te [*LSRC-Tunnel21] destination 1.1.1.1 [*LSRC-Tunnel21] mpls te tunnel-id 201 [*LSRC-Tunnel21] mpls te signal-protocol cr-static [*LSRC-Tunnel21] mpls te passive-tunnel [*LSRC-Tunnel21] mpls te binding bidirectional static-cr-lsp egress lsp2 [*LSRC-Tunnel21] commit [~LSRC-Tunnel21] quit
- Configure an MPLS TE tunnel protection group.# On LSRA, configure a tunnel protection group that consists of a working tunnel named Tunnel 10 and its protection tunnel named Tunnel 11.
[~LSRA] interface Tunnel 10 [*LSRA-Tunnel10] mpls te protection tunnel 101 mode revertive wtr 0 [*LSRA-Tunnel10] commit [~LSRA-Tunnel10] quit
# On LSRC, configure a tunnel protection group that consists of a working tunnel named Tunnel 20 and its protection tunnel named Tunnel 21.
[~LSRC] interface Tunnel 20 [*LSRC-Tunnel20] mpls te protection tunnel 201 mode revertive wtr 0 [*LSRC-Tunnel20] commit [~LSRC-Tunnel20] quit
- Configure a detection mechanism to monitor the configured tunnel protection group. MPLS-TP OAM is used in this example.On LSRA, configure MPLS-TP OAM on Tunnel 10.
[~LSRA] mpls-tp meg abc [~LSRA-mpls-tp-meg-abc] me te interface Tunnel10 mep-id 1 remote-mep-id 2 [*LSRA-mpls-tp-meg-abc] commit [~LSRA-mpls-tp-meg-abc] quit
On LSRC, configure MPLS-TP OAM on Tunnel 20.[~LSRC] mpls-tp meg abc [~LSRC-mpls-tp-meg-abc] me te interface Tunnel20 mep-id 2 remote-mep-id 1 [*LSRC-mpls-tp-meg-abc] commit [~LSRC-mpls-tp-meg-abc] quit
- Verify the configuration.
After completing the configuration, run the display mpls te protection tunnel all verbose command on LSRA. The command output shows that the tunnel interfaces are working properly.
# Check the configuration results on LSRA.[~LSRA] display mpls te protection tunnel all verbose ---------------------------------------------------------------- Verbose information about the No."1" protection-group ---------------------------------------------------------------- Work-tunnel id : 100 Protect-tunnel id : 101 Work-tunnel name : Tunnel10 Protect-tunnel name : Tunnel11 Work-tunnel reverse-lsp : - Protect-tunnel reverse-lsp : - Bridge type : 1:1 Switch type : bidirectional Switch result : work-tunnel Tunnel using Best-Effort : none Tunnel using Ordinary : none Work-tunnel frr in use : none Work-tunnel defect state : non-defect Protect-tunnel defect state : non-defect Work-tunnel forward-lsp defect state : non-defect Protect-tunnel forward-lsp defect state : non-defect Work-tunnel reverse-lsp defect state : non-defect Protect-tunnel reverse-lsp defect state : non-defect HoldOff config time : 0ms HoldOff remain time : - WTR config time : 0s WTR remain time : - Mode : revertive Using same path : - Local state : no request Far end request : no request
Configuration Files
LSRA configuration file
# sysname LSRA # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls mpls te # bidirectional static-cr-lsp ingress Tunnel10 forward nexthop 2.1.1.2 out-label 20 backward in-label 20 # bidirectional static-cr-lsp ingress Tunnel11 forward nexthop 4.1.1.2 out-label 21 backward in-label 21 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 2.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 4.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel10 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 3.3.3.3 mpls te signal-protocol cr-static mpls te tunnel-id 100 mpls te bidirectional mpls te protection tunnel 101 mode revertive wtr 0 # interface Tunnel11 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 3.3.3.3 mpls te signal-protocol cr-static mpls te tunnel-id 101 mpls te bidirectional # ip route-static 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 2.1.1.2 ip route-static 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 2.1.1.2 ip route-static 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 4.1.1.2 ip route-static 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 4.1.1.2 # mpls-tp meg abc me te interface Tunnel10 mep-id 1 remote-mep-id 2 # return
LSRB configuration file
# sysname LSRB # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls mpls te # bidirectional static-cr-lsp transit lsp1 forward in-label 20 nexthop 3.2.1.2 out-label 40 backward in-label 16 nexthop 2.1.1.1 out-label 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 2.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 3.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 2.1.1.1 ip route-static 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 3.2.1.2 # return
LSRC configuration file
# sysname LSRC # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls mpls te # bidirectional static-cr-lsp egress lsp1 forward in-label 40 lsrid 1.1.1.1 tunnel-id 100 backward nexthop 3.2.1.1 out-label 16 # bidirectional static-cr-lsp egress lsp2 forward in-label 41 lsrid 1.1.1.1 tunnel-id 101 backward nexthop 3.4.1.1 out-label 17 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 3.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 3.4.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel20 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 1.1.1.1 mpls te signal-protocol cr-static mpls te tunnel-id 200 mpls te passive-tunnel mpls te binding bidirectional static-cr-lsp egress lsp1 mpls te protection tunnel 201 mode revertive wtr 0 # interface Tunnel21 ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack1 tunnel-protocol mpls te destination 1.1.1.1 mpls te signal-protocol cr-static mpls te tunnel-id 201 mpls te passive-tunnel mpls te binding bidirectional static-cr-lsp egress lsp2 # ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 3.2.1.1 ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 3.4.1.1 ip route-static 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 3.2.1.1 ip route-static 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 3.4.1.1 # mpls-tp meg abc me te interface Tunnel20 mep-id 2 remote-mep-id 1 # return
LSRD configuration file
# sysname LSRD # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4 # mpls mpls te # bidirectional static-cr-lsp transit lsp2 forward in-label 21 nexthop 3.4.1.2 out-label 41 backward in-label 17 nexthop 4.1.1.1 out-label 21 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 4.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 3.4.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls te # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 # ip route-static 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 4.1.1.1 ip route-static 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 3.4.1.2 # return