Association Between CR-LSP Establishment and the IS-IS Overload
An association between constraint-based routed label switched path (CR-LSP) establishment and IS-IS overload enables the ingress to establish a CR-LSP that excludes overloaded IS-IS nodes. The association ensures that MPLS TE traffic travels properly along the CR-LSP, therefore improving CR-LSP reliability and service transmission quality.
Background
If a device is unable to store new link state protocol data units (LSPs) or use LSPs to update its link state database (LSDB) information, the device will calculate incorrect routes, causing forwarding failures. The IS-IS overload function enables the device to set the device to the IS-IS overload state to prevent such forwarding failures. By configuring the ingress to establish a CR-LSP that excludes the overloaded IS-IS device, the association between CR-LSP establishment and the IS-IS overload function helps the CR-LSP reliably transmit MPLS TE traffic.
Related Concepts
IS-IS overload state
When a device cannot store new LSPs or use LSPs to update its LSDB information using LSPs, the device will incorrectly calculate IS-IS routes. In this situation, the device will enter the overload state. For example, an IS-IS device becomes overloaded if its memory resources decrease to a specified threshold or if an exception occurs on the device. A device can be manually configured to enter the IS-IS overload state.
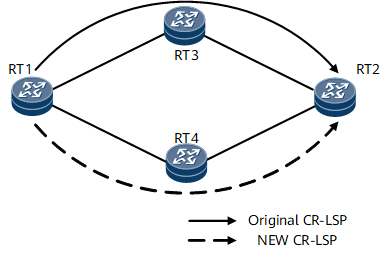
Implementation
- If RT3 enters the IS-IS overload state, IS-IS propagates packets carrying overload information in the IS-IS area.
- RT1 determines that RT3 is overloaded and re-calculates the CR-LSP destined for RT2.
- RT1 calculates a new path RT1 -> RT4 - >RT2, which bypasses the overloaded IS-IS node. Then RT1 establishes a new CR-LSP along this path.
- After the new CR-LSP is established, RT1 switches traffic from the original CR-LSP to the new CR-LSP, ensuring service transmission quality.