P2MP TE Applications for Multicast Services
Service Overview
There is an increasing diversity of multicast services, such as Internet Protocol Television (IPTV), multimedia conferencing, and real-time online multi-player gaming. These services require the bearer network to have the following capabilities:
- Normally and smoothly forward multicast traffic even during traffic congestion.
- Rapidly detect network faults and switch traffic to a backup link if the primary link fails.
Networking Description
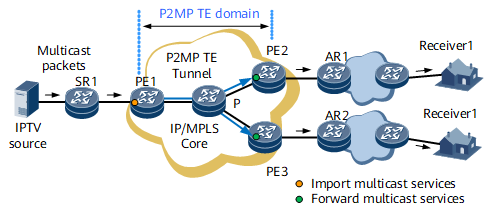
Point-to-multipoint (P2MP) traffic engineering (TE) is deployed on an IP/MPLS backbone network to resolve multicast traffic congestion and maintain reliability. Figure 1 shows the application of P2MP TE for multicast services on an IP/MPLS backbone network.
Feature Deployment
The deployment of P2MP TE for IP multicast services involves the following aspects:
-
Deploy PIM on the P2MP TE tunnel interfaces of the ingress (PE1). Configure multicast static groups to import multicast traffic to P2MP TE tunnels.
-
The following tunnel deployment scheme is recommended:
- Path planning: Configuring explicit paths is recommended. Prevent the re-merge and cross-over problems during path planning.
- Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) authentication: Configure RSVP neighbor-based authentication to improve the protocol security of the backbone network.
- RSVP Srefresh: Configure RSVP Srefresh to improve the resource utilization of the backbone network.
- P2MP TE FRR: Configure FRR to improve the reliability of the backbone network.
- Multicast traffic forwarding
- Configure PIM on the egresses (PE2 and PE3) to generate multicast forwarding entries. Configure the devices to ignore reverse path forwarding (RPF) check.
- An egress cannot forward a received multicast data message of an any-source multicast (ASM) group if the RPF check result shows that the egress is neither directly connected to the multicast source nor the rendezvous point (RP) of the multicast group. To enable downstream hosts to receive the message in such a case, deploy multicast source proxy, which enables the egress to send a Register message to the RP (for example, SR1) in the PIM domain. The data message can then be forwarded along an RPT.