Configuring VPLS Multi-Homing
In VPLS networking in which a CE is multi-homed to multiple PEs, configuring VPLS multi-homing prevents routing loops between the multi-homed CE and its connected PEs.
Usage Scenario
To deliver high-reliability services over a VPLS network, carriers usually dual-home a CE to two PEs through redundant links. While providing link-level protection, the dual-homing mechanism also brings in the risk of routing loops. To prevent routing loops in multi-homing scenarios, you can deploy VPLS multi-homing on PEs.
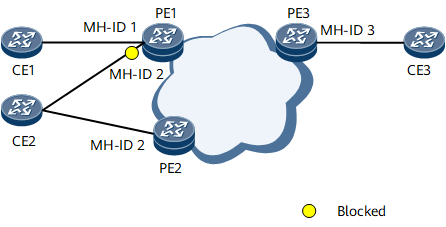
A PE assigns a multi-homing site and MH-ID to each accessed CE in a VSI, and shares a default multi-homing site with a single-homed CE. If a CE is dual-homed to PE1 and PE2, they must assign the same MH-ID to the CE. On the network shown in Figure 1, PE1 assigns a multi-homing site and MH-ID 1 to CE1. CE2 is dual-homed to PE1 and PE2, which both assign MH-ID 2 to CE2. VPLS multi-homing adjusts link priorities based on the AC status (ACS), multi-homing site priority (PREF), and PE's router ID (PE-ID) in descending order of priority to ensure that one access link of a multi-homed CE is in the active state and the other access links are in the blocked state.

VPLS multi-homing described in this document cannot work together with VPLS multi-homing defined in the draft-ietf-bess-vpls-multihoming-00 standard.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring VPLS multi-homing, complete the following tasks:
Configure interface IP addresses and an IGP on PEs and Ps.
Configure LSR IDs and basic MPLS functions on PEs and Ps.
Establish MPLS tunnels between the PEs to transmit service data.
(Optional) Configuring Basic EFM OAM Functions or Configuring Basic CFM Functions if EFM or CFM is deployed between the CE and PE.
- Configuring PEs to Exchange VPLS Information as BGP Peers
- BGP VPLS inherits most BGP configurations and shares TCP connections with BGP. A major difference between BGP and BGP VPLS is that BGP VPLS requires PEs to exchange VPLS information as BGP peers in the L2VPN-AD address family view.
- Creating a VPLS Connection
- When configuring VPLS multi-homing, create VSIs, configure BGP signaling, RDs, and VPN targets, and create VPLS connections.
- Binding a Multi-homing Site to an AC Interface
- Configure an AC interface and bind a multi-homing site to the AC interface to implement VPLS multi-homing.
- Verifying the VPLS Multi-Homing Configuration
- After configuring VPLS multi-homing, check VSI and VPLS connection information.