Configuring PW APS
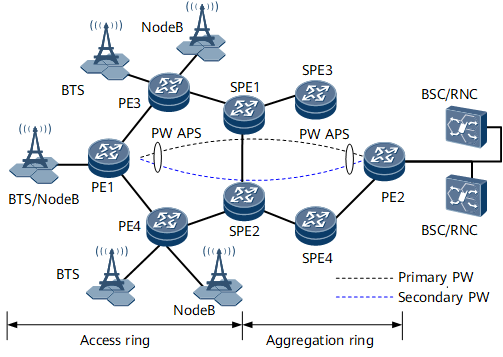
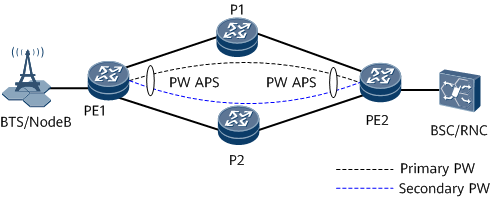
Pseudo wire (PW) automatic protection switching (APS) applies to scenarios where the primary and secondary PWs share the same source and same destination.

This chapter applies only to the NetEngine 8000 F1A.
Context
In a PW APS scenario, PW OAM detects the status of the active and standby PWs. When PW OAM detects a fault on the active PW, it immediately notifies PW APS of the fault, which is then triggered to perform an active/standby PW switchover. The PWs can be classified as single-segment PWs (SS-PWs) or multi-segment PWs (MS-PWs) or be classified as dynamic PWs or static PWs. See Figure 1 and Figure 2.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring PW protection, complete the following tasks:
Configure IP addresses and an IGP on PEs.
Establish public network tunnels or between PEs. The public network tunnels can be:
LDP tunnel: To establish an LDP tunnel, you must enable MPLS and MPLS LDP both globally and per interface on each public network node along the tunnel. If two PEs are indirectly connected, establish a remote LDP session between them.
TE tunnel: To establish a TE tunnel, you must enable MPLS, MPLS TE, and RSVP-TE both globally and per interface on each public network node along the tunnel, and enable CSPF in the MPLS view of the tunnel ingress.

Because pseudo wire emulation edge-to-edge (PWE3) uses LDP to distribute VPN labels, you must globally enable MPLS LDP on PEs and establish remote MPLS LDP sessions if TE tunnels are used as public network tunnels.
If the public network tunnels are not LDP tunnels, you must configure tunnel policies and apply them to these tunnels.
Enable MPLS L2VPN on PEs.
- Configuring a PW Protection Group
- In a PW APS scenario, a PW protection group consists of primary and secondary PWs. The PWs can be either SS-PWs or MS-PWs.
- Configuring a PW APS Instance and Bind a PW Protection Group to the PW APS Instance
- The state machine of a PW APS instance determines the protection switching in PW protection groups associated with the instance.
- Configuring PW OAM to Detect Public Network Link Faults
- PW OAM includes Multiprotocol Label Switching Transport Profile (MPLS-TP) OAM and MPLS OAM. PW OAM can quickly detect PW faults, enabling speedy PW switchovers for service protection.
- (Optional) Configuring PW APS Parameters
- This section describes how to configure PW APS parameters, such as the switchback mode, hold time for PW switchover, and WTR time for PW switchback. In network O&M, you can manually trigger PW switching with commands.
- Verifying the PW APS Configuration
- After you complete the configurations, check information about the PW APS instance and its associated PW protection groups.