Configuring IPv6 VXLAN in Distributed Gateway Mode Using BGP EVPN
Distributed IPv6 VXLAN gateways can be configured to address problems that occur in centralized gateway networking. Such problems include sub-optimal forwarding paths and bottlenecks on Layer 3 gateways in terms of ARP or ND entry specifications.
Usage Scenario
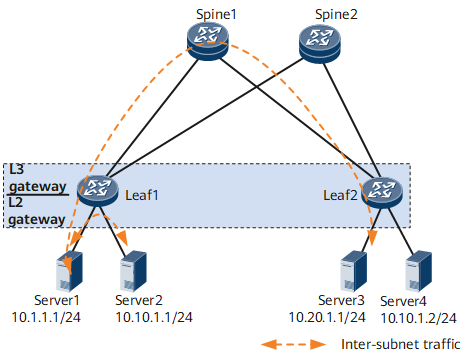
On the network shown in Figure 1, Server1 and Server2 on different subnets both connect to Leaf1. When Server1 and Server2 communicate, traffic is forwarded only through Leaf1, not through any spine node.
Flexible deployment. A leaf node can function as both Layer 2 and Layer 3 IPv6 VXLAN gateways.
Improved network expansion capabilities. Unlike a centralized Layer 3 gateway, which has to learn the ARP or ND entries of all servers on a network, a distributed gateway needs to learn the ARP or ND entries of only the servers attached to it. This addresses the problem of the ARP or ND entry specifications being a bottleneck for packet forwarding.
Either IPv4 or IPv6 addresses can be configured for the VMs and Layer 3 VXLAN gateway. This means that a VXLAN overlay network can be an IPv4 or IPv6 network. Figure 1 shows an IPv4 overlay network.

If only VMs on the same subnet need to communicate with each other, Layer 3 IPv6 VXLAN gateways do not need to be deployed. If VMs on different subnets need to communicate with each other or VMs on the same subnet need to communicate with external networks, Layer 3 IPv6 VXLAN gateways must be deployed.
Configuration Task |
IPv4 Overlay Network |
IPv6 Overlay Network |
|---|---|---|
Configure a VPN instance for route leaking with an EVPN instance. |
Enable the IPv4 address family of the involved VPN instance and then complete other configurations in the VPN instance IPv4 address family view. |
Enable the IPv6 address family of the involved VPN instance and then complete other configurations in the VPN instance IPv6 address family view. |
Configure a Layer 3 gateway on an IPv6 VXLAN. |
Configure an IPv4 address for the VBDIF interface of the Layer 3 gateway. |
Configure an IPv6 address for the VBDIF interface of the Layer 3 gateway. |
Configure IPv6 VXLAN gateways to exchange specific types of routes. |
|
|
- Configuring a VXLAN Service Access Point
- On an IPv6 VXLAN, Layer 2 sub-interfaces are used for service access and can have different encapsulation types configured to transmit various types of data packets. After a Layer 2 sub-interface is associated with a BD, which is used as a broadcast domain on the IPv6 VXLAN, the sub-interface can transmit data packets through this BD.
- Configuring an IPv6 VXLAN Tunnel
- Using BGP EVPN to establish an IPv6 VXLAN tunnel between VTEPs involves a series of operations. These include establishing a BGP EVPN peer relationship, configuring an EVPN instance, and configuring ingress replication.
- (Optional) Configuring a VPN Instance for Route Leaking with an EVPN Instance
- To enable communication between VMs on different subnets, configure a VPN instance for route leaking with an EVPN instance. This configuration enables Layer 3 connectivity. To isolate multiple tenants, you can use different VPN instances.
- (Optional) Configuring a Layer 3 Gateway on the IPv6 VXLAN
- To enable communication between VMs on different subnets, configure Layer 3 gateways on the IPv6 VXLAN, enable the distributed gateway function, and configure host route advertisement.
- (Optional) Configuring IPv6 VXLAN Gateways to Advertise Specific Types of Routes
- To enable communication between VMs on different subnets, configure IPv6 VXLAN gateways to exchange IRB or IP prefix routes. This configuration enables the gateways to learn the IP routes of the related hosts or the subnets where the hosts reside.
- (Optional) Configuring a Limit on the Number of MAC Addresses Learned by an Interface
- MAC address learning limiting helps improve VXLAN network security.
- Verifying the Configuration
- After configuring IPv6 VXLAN in distributed gateway mode using BGP EVPN, verify information about the IPv6 VXLAN tunnels, VNI status, and VBDIF interfaces.