mLDP Applications in an IPTV Scenario
Service Overview
The IP or Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) technology has become a mainstream bearer technology on backbone networks, and the demands for multicast services (for example, IPTV) transmitted over bearer networks are evolving. Carriers draw on the existing MPLS mLDP technique to provide the uniform MPLS control and forwarding planes for multicast services transmitted over backbone networks.
Networking Description
Feature Deployment
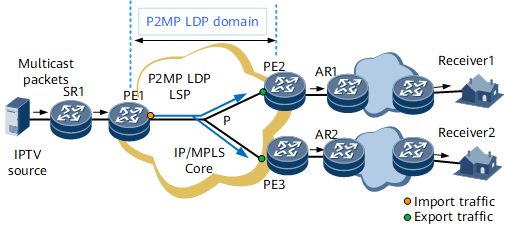
Establish an mLDP LSP.
Perform the following steps:- Plan the root, transit, and leaf nodes on an mLDP LSP.
- Configure leaf nodes to send requests to the root node to establish point-to-multipoint (P2MP) LDP LSPs.
- Configure a virtual tunnel interface and bind the LSP to it.
Import multicast services into the LSP.
Configure the quality of service (QoS) redirection function on the ingress PE1 to direct data packets sent by a multicast source to the specified mLDP LSP.
Forward multicast services.
To enable the egresses (PE2 and PE3) to forward multicast services, perform the following operations:
Configure the egresses to run Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) to generate multicast forwarding entries.
Enable the egresses to ignore the Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (URPF) check.
This is because the URPF check fails as PIM does not need to be run on core nodes on the P2MP LDP network.
Enable multicast source proxy based on the location of the Rendezvous Point (RP).
After multicast data packets for a multicast group in an any-source multicast (ASM) address range are directed to an egress, the egress checks the packets based on unicast routes. Multicast source proxy is enabled or disabled based on the following check results:
- If the egress is indirectly connected to a multicast source and does not function as the RP to which the group corresponds, the egress stops forwarding multicast data packets. As a result, downstream hosts cannot receive these multicast data packets. Multicast source proxy can be used to address this problem. Multicast source proxy enables the egress to send a Register message to the RP deployed on a source-side device (for example, SR1) in a PIM domain. The RP adds the egress to a rendezvous point tree (RPT) to enable the egress to forward multicast data packets to the downstream hosts.
If the egress is directly connected to a multicast source or functions as the RP to which the group corresponds, the egress can forward multicast data packets, without multicast source proxy enabled.