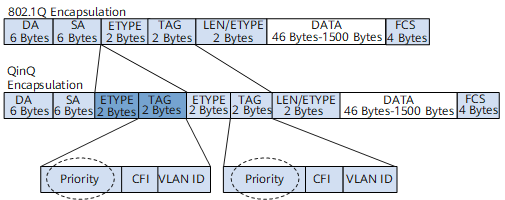
802.1p on a QinQ Interface
During QinQ encapsulation, a QinQ interface adds an outer VLAN tag to the packet it received and is unaware of the 802.1p value in the inner VLAN tag. As a result, the service priority identified by the 802.1p value is ignored. Figure 1 shows the 802.1p field in a QinQ packet.
To solve this problem, the 802.1p value in the inner VLAN tag must be processed on a QinQ sub-interface. The following three ways are available on a QinQ interface:
Ignores the 802.1p value in the inner VLAN tag, but resets the 802.1p value in the outer VLAN tag.
Automatically maps the 802.1p value in the inner VLAN tag to an 802.1p value in the outer VLAN tag.
Sets the 802.1p value in the outer VLAN tag according to the 802.1p value in the inner VLAN tag.
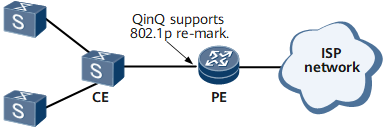
In Figure 2, QinQ supports 802.1p in following modes:
Pipe mode: A specified 802.1p value is set.
Uniform mode: The 802.1p value in the inner VLAN tag is used.
Maps the 802.1p value in the inner VLAN tag to an 802.1p value in the outer VLAN tag. Multiple 802.1p values in the inner VLAN tag can be mapped to an 802.1p value in the outer VLAN tag, but one 802.1p value in the inner VLAN tag cannot be mapped to multiple 802.1p values in the outer VLAN tag.