MPLS-based VPN
A traditional virtual private network (VPN) transmits private network data over a public network using tunneling protocols, such as the Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE), Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP), and Point to Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP).
An MPLS-based VPN, which is as secure as Frame Relay networks, does not encapsulate or encrypt packets; therefore, IP Security (IPsec), GRE, or L2TP tunnels do not need to be deployed. The MPLS-based VPN helps minimize the network delay time.
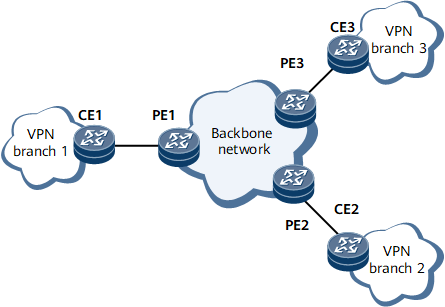
The MPLS-based VPN connect different branches of the private network through LSPs to form a unified network, as shown in Figure 1. The MPLS-based VPN also supports interworking between different VPNs.
Figure 1 illustrates an MPLS-based VPN. The following devices are deployed on the MPLS-based VPN:
Customer edge (CE): an edge device on a customer network. The CE can be a router, switch, or host.
Provider edge (PE): an edge device on a service provider network.
- Provider (P): is a backbone device in the service provider network and does not connect to CEs directly. A P device obtains basic MPLS forwarding capabilities but does not maintain VPN information.
The principles of an MPLS-based VPN are as follows:
PEs manage VPN users, establish LSPs between themselves, and advertise routes to VPN sites.
LDP or MP-BGP is used to allocate routes.
The MPLS-based VPN supports IP address multiplexing between sites and the interconnection of VPNs.