MLD On-Demand
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) on-demand helps to maintain MLD group memberships and frees a multicast device and its connected access device from exchanging a large number of packets.
Background
When a multicast device is directly connected to user hosts, the multicast device sends MLD Query messages to and receives MLD Report and Done messages from the user hosts to identify the multicast groups that have attached receivers on the shared network segment.
The device directly connected to a multicast device, however, may not be a host but an MLD proxy-capable access device to which hosts are connected. If you configure only MLD on the multicast device, access device, and hosts, the multicast and access devices need to exchange a large number of packets.
To resolve this problem, enable MLD on-demand on the multicast device. The multicast device sends only one general query message to the access device. After receiving the general query message, the access device sends the collected Join and Leave status of multicast groups to the multicast device. The multicast device uses the Join and Leave status of the multicast groups to maintain multicast group memberships on the local network segment.
Benefits
MLD on-demand reduces packet exchanges between a multicast device and its connected access device and reduces the loads of these devices.
Related Concepts
MLD on-demand
MLD on-demand enables a multicast device to send only one MLD general query message to its connected access device (MLD proxy-capable) and to use Join/Leave status of multicast groups reported by its connected access device to maintain MLD group memberships.
Implementation
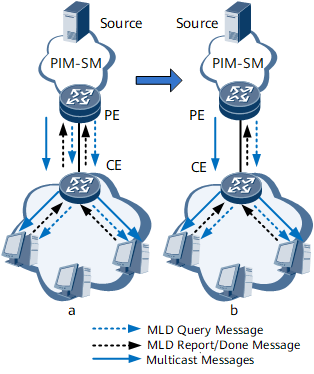
On the network a shown in Figure 1, if MLD on-demand is not enabled on the PE, the PE sends a large number of MLD Query messages to the CE, and the CE sends a large number of Report and Done messages to the PE. As a result, lots of PE and CE resources are consumed.
On the network b shown in Figure 1, after MLD on-demand is enabled on the PE, the PE sends only one general query message to the CE. After receiving the general query message from the PE, the CE sends the collected Join and Leave status of MLD groups to the PE. The CE sends a Report or Done message for a group to the PE only when the Join or Leave status of the group changes. To be specific, the CE sends an MLD Report message for a multicast group to the PE only when the first user joins the multicast group and sends a Done message only when the last user leaves the multicast group.

The records on dynamically joined multicast groups on the multicast device interface connected to the access device do not time out.
The multicast device interface connected to the access device sends only one MLD general query message to the access device.
The multicast device interface connected to the access device directly deletes the entry for a group after it receives an MLD Done message for the group.