Validity Check of ARP Packets
Background
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol used for resolution of network layer addresses into link layer addresses. It is easy to implement, but does not have any security mechanisms. Therefore, it is vulnerable to attacks. Attackers can forge ARP packets by modifying media access control (MAC) addresses carried in the Data fields of ARP packets sent from authorized users. This process makes the source and destination MAC addresses carried in the Data field different from those carried in the Ethernet header.
This problem can be solved by configuring a validity check of ARP packets on devices. When a device capable of checking ARP packet validity receives an ARP packet, the device checks whether the source and destination MAC addresses carried in the Data field match those carried in the Ethernet header. If they match, the packet is considered valid and allowed to pass through. If they do not match, the device considers the packet an attack packet and discards it.
Related Concepts
Source MAC addresses After receiving an ARP packet, the device checks whether the source MAC address in the Data field matches that in the Ethernet header. If they match, the device considers the packet valid and allows it to pass through. If they do not match, the device considers the packet an attack packet and discards it.
- Destination MAC addresses (only for ARP reply packets)
- After receiving an ARP packet, the device checks the destination MAC address in the Data field. If the destination MAC address is all 1s, the device considers the ARP packet an attack packet and discards it.
- After receiving an ARP packet, the device checks whether the destination MAC address in the Data field matches that in the Ethernet header. If they match, the device considers the packet valid and allows it to pass through. If they do not match, the device considers the packet an attack packet and discards it.
- Source and destination MAC addresses
- After receiving an ARP request packet, the device checks whether the source and destination MAC addresses in the Data field match those in the Ethernet header. If they match, the device considers the packet valid and allows it to pass through. If they do not match, the device considers the packet an attack packet and discards it.
- After receiving an ARP reply packet, the device checks whether the source and destination MAC addresses in the Data field match those in the Ethernet header and whether the destination MAC address is all 1s. If the source and destination MAC addresses in the Data field match those in the Ethernet header and the destination MAC address is not all 1s, the device considers the packet valid and allows it to pass through. Otherwise, the device considers the packet an attack packet and discards it.
Implementation
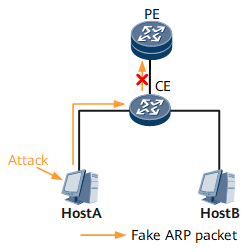
In the example in Figure 1, host A is attacked, and the attacker modifies the source MAC address of the ARP request packet. As a result, in the ARP request packet that host A sends, the source MAC address in the Data field of the packet is different from that in the Ethernet header of the packet. If validity check of ARP packets is not enabled, both host B and provider edge (PE) learn the fake address information carried in the ARP request packet from host A.
If validity check of ARP packets is configured on the PE, and the PE receives an ARP request packet, the PE checks whether the source MAC address in the Data field of the ARP request packet matches that in the Ethernet header. If they match, the PE learns the address information carried in the packet. If they do not match, the PE discards the packet.
Usage Scenario
Validity check of ARP packets is deployed on access devices.
Benefits
Validity check of ARP packets protects devices against ARP packets sent from authorized users that have been attacked. Therefore, network security and reliability are improved.