Static Route Permanent Advertisement
Background
When the link over which a static route runs fails, the static route will be deleted from the IP routing table to trigger a route re-selection. After a new route is selected, traffic is switched to the new route. Some carriers, however, may require that specific traffic always travel along a fixed link, regardless of the link status. Static route permanent advertisement is introduced to meet this service need.
Implementation
With static route permanent advertisement, a static route can still be advertised and added to the IP routing table for route selection even when the link over which the static route runs fails. After static route permanent advertisement is configured, the static route can be advertised and added to the IP routing table in both of the following scenarios:
An outbound interface is configured for the static route, and the outbound interface has an IP address. Static route permanent advertisement is not affected no matter whether the outbound interface is Up.
No outbound interface is configured for the static route. Static route permanent advertisement is not affected no matter whether the static route can obtain an outbound interface through route recursion.

After static route permanent advertisement is enabled, a static route always remains in the IP routing table regardless of route reachability. If the destination of the route becomes unreachable, traffic interruption occurs.
Typical Networking
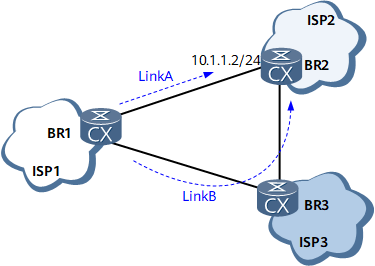
On the network shown in Figure 1, BR1, BR2, and BR3 belong to ISP1, ISP2, and ISP3 respectively. Two links (Link A and Link B) exist between BR1 and BR2, but ISP1 expects its service traffic destined for ISP2 to be always transmitted over Link A.
A direct EBGP peer relationship is established between BR1 and BR2. A static route is created on BR1, with 10.1.1.2/24 (IP address of BR2) as the destination address and the local interface connected to BR2 as the outbound interface.
Without static route permanent advertisement, Link A is used to transmit traffic. If Link A fails, BGP will switch the traffic to Link B.
With static route permanent advertisement, Link A is used to transmit traffic regardless of whether the destination is reachable through Link A. If Link A fails, no link switchover is performed, causing traffic interruption. To check whether the destination is reachable through the static route, ping the destination address of the static route to which static route permanent advertisement is applied.