Vlink Direct Route Advertisement
Background
By default, IPv4 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Vlink direct routes or IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) Vlink direct routes are only used for packet forwarding in the same VLAN and cannot be imported to dynamic routing protocols. This is because importing Vlink direct routes to dynamic routing protocols will increase the number of routing entries and affect routing table stability. In some cases, some operations need to be performed based on Vlink direct routes of VLAN users. For example, different VLAN users use different route exporting policies to guide traffic from the remote device. In this scenario, ARP or NDP Vlink direct routes are needed to be imported by a dynamic routing protocol and advertised to the remote device. After advertisement of ARP or NDP Vlink direct routes is enabled, these direct routes can be imported by a dynamic routing protocol (IGP or BGP) and advertised to the remote device.
Related Concepts
ARP Vlink direct routes: routing entries with physical interfaces of VLAN users and used to forward IP packets. These physical interfaces are learned using ARP. On networks with VLANs, IP packets can be forwarded only by physical interfaces rather than logical interfaces. After learning the ARP entry of a peer end, VLANIF interfaces, QinQ interfaces, or QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces generate a 32-bit ARP Vlink direct route, and the route is displayed in the routing table. Regular physical interfaces do not generate a 32-bit ARP Vlink direct route in this case.
NDP Vlink direct routes: routing entries carrying IPv6 addresses of VLAN users' physical interfaces. These IPv6 addresses are learned and resolved using NDP.
Implementation
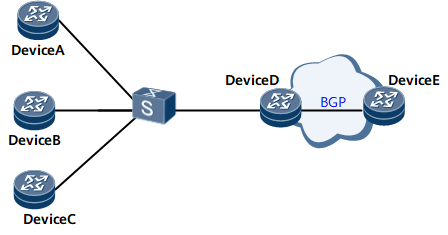
On the network shown in Figure 1, Device A, Device B, and Device C are connected to the logical interface of Device D which is a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) peer of Device E. However, Device E needs to communicate only with Device B rather than Device A and Device C. In this scenario, Vlink direct route advertisement must be enabled on Device D. Then Device D obtains each physical interface of Device A, Device B, and Device C, uses a routing policy to filter out network segment routes and routes destined for Device A and Device C, and advertises the route destined for Device B to Device E.
Usage Scenario
Vlink direct route advertisement is applicable to networks in which a device needs to add Vlink direct routes with physical interfaces of VLAN users to the routing table of a dynamic routing protocol before advertising the routes to remote ends.
Advantages
With Vlink direct route advertisement, a device can add Vlink direct routes to the routing table of a dynamic routing protocol (such as an Interior Gateway Protocol or BGP) and then use different export policies to advertise routes required by remote ends.