MAC Flapping-based Loop Detection for VPLS Networks
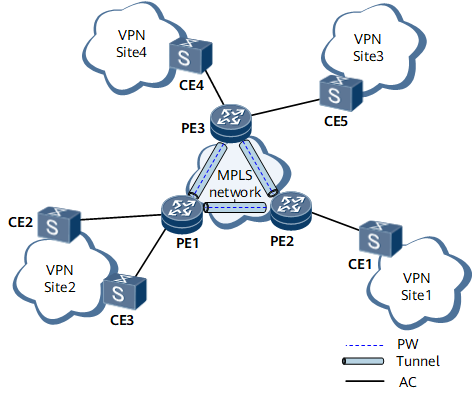
On the virtual private LAN service (VPLS) network shown in Figure 1, pseudo wires (PWs) are established over Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) tunnels between virtual private network (VPN) sites to transparently transmit Layer 2 packets. When forwarding packets, the provider edges (PEs) learn the source MAC addresses of the packets, create MAC address entries, and establish mapping between the MAC addresses and AC interfaces and mapping between the MAC addresses and PWs.
- Blocking interfaces based on their blocking priorities: If a device detects a loop, it blocks the interface with a lower blocking priority.
- Blocking interfaces based on their trusted or untrusted states: If a device detects a loop, it blocks the untrusted interface.
MAC flapping-based loop detection can also detect PW-side loops. The principles of blocking PWs are similar to those of blocking AC interfaces.
In addition, MAC flapping-based loop detection can associate an interface with its sub-interfaces bound with virtual switching instances (VSIs). If a loop occurs in the VSI bound to a sub-interface, the sub-interface is blocked. However, a loop may also exist in a VSI bound to another sub-interface. If the loop is not eliminated in time, it will cause traffic congestion or even a network breakdown. To inform the network administrator of loops, enable MAC flapping-based loop detection association on the interface of the sub-interfaces bound with VSIs. In this situation, if a sub-interface bound with a VSI is blocked due to a loop, the interface on which the sub-interface is configured is also blocked and an alarm is generated. After that, all the other sub-interfaces bound with VSIs are blocked.