VRP8 High Extensibility
To improve extensibility, the VRP8 supports backward compatibility and plug-and-play functionality on hardware line cards, allowing quick responses to users' demands. The VRP8 implements high expandability for the following items:
- Line cards: Standard driver framework and plug-and-play are supported.
- Software features: The data plane operates based on modules.
- Capacity and performance: Services based on fine-granularity distribution are simultaneously processed.
- Operation and maintenance tools: The configuration plane is separated from the control plane.
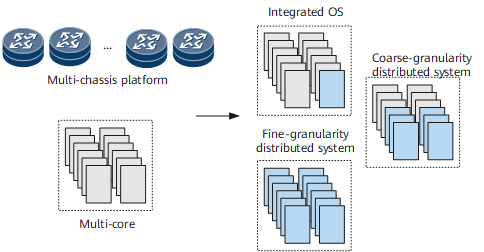
The trend is to utilize, multi-main control board, multi-CPU, and multi-core architectures in the development of the hardware on existing core routers. The reason is that traditional integrated OS does not support modular service deployment or processing, and only depends on the processing capability of a single CPU with a single core. The second-generation OS supports coarse-granularity modules, allowing multiple protocols and service modules to simultaneously process services. These OSs, however, are incapable of supporting the processing of protocol- and service-specific distributed instances and are still unable to take advantage of multi-CPU and multi-core processing capabilities. The VRP8 with its fine-granularity distributed architecture and protocol- and service-specific components allows a device to deploy services in distributed instances and to process services simultaneously. This helps a device overcome the constraints of the single entity's processing capability and memory and to take advantage of integral hardware processing capability on the control plane, improving the sustainable extensibility of the device's performance and capacity.
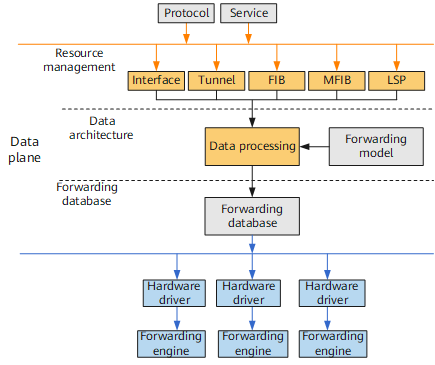
On the VRP8, the data plane adopts a model-based data processing technique. A mere change in the forwarding model, not in code, allows a new function to be implemented or allows a function change on the forwarding plane, enabling quick responses to carriers' demands.