Application Scenarios for MSDP
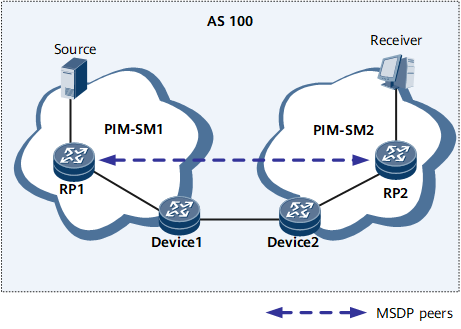
Inter-Domain Multicast
An MSDP peer relationship is set up between rendezvous points (RPs) in two different PIM-SM domains. Multicast source information can then be shared between the two domains.
After multicast data reaches RP 1 (the source's RP), RP 1 sends a source active (SA) message that carries the multicast source information to RP 2.
RP 2 initiates a shortest path tree (SPT) setup request to the source.
RP 2 forwards the multicast data to the receiver in the local domain.
After Receiver receives the multicast data, it independently determines whether to initiate an SPT switchover.
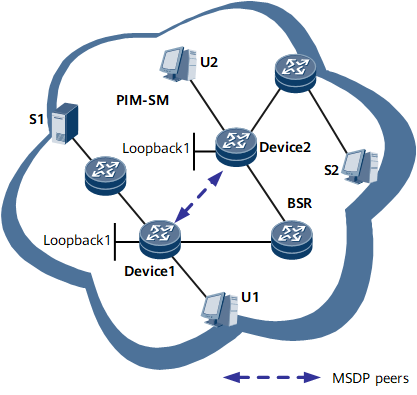
Anycast-RP
Device 1 and Device 2 function as RPs and establish an MSDP peer relationship between each other.
Intra-domain multicast is performed using this MSDP peer relationship. A receiver sends a Join message to the nearest RP to set up a rendezvous point tree (RPT).
The multicast source registers with the nearest RP. RPs exchange SA messages to share the multicast source information.
Each RP joins an SPT with the source's DR at the root.
After receiving the multicast data, the receiver decides whether to initiate an SPT switchover.