IPRAN Applications of Association Between Direct Routes and a VRRP Group
Service Overview
NodeBs and radio network controllers (RNCs) on an IP radio access network (RAN) do not have dynamic routing capabilities. Therefore, static routes must be configured to allow NodeBs to communicate with aggregation site gateways (ASGs) and allow RNCs to communicate with remote service gateways (RSGs) that are at the aggregation layer. VRRP is configured to provide ASG and RSG redundancy, improving device reliability and ensuring non-stop transmission of value-added services, such as voice, video, and cloud computation services over mobile bearer networks.
Networking Description
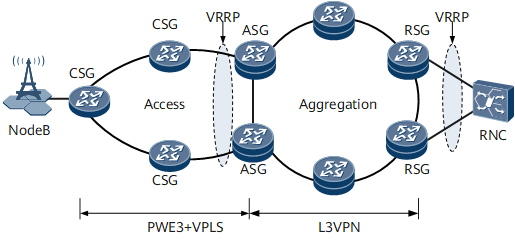
Figure 1 shows VRRP-based gateway protection applications on an IPRAN. A NodeB is dual-homed to VRRP-enabled ASGs to communicate with the aggregation network. The NodeB sends traffic destined for the RNC through the master ASG, whereas the RNC sends traffic destined for the NodeB through either the master or backup ASG over a path selected by a dynamic routing protocol. As a result, traffic in opposite directions may travel along different paths. Similarly, the RNC is dual-homed to VRRP-enabled RSGs. Path inconsistency may also occur.
Feature Deployment
On the IPRAN shown in Figure 1, both ASGs and RSGs may send and receive traffic over different paths. For example, user-to-network traffic enters the aggregation network through the master ASG, whereas network-to-user traffic flows out of the aggregation network from the backup ASG. Path inconsistency complicates traffic monitoring or statistics collection and increases the cost. In addition, when the master ASG is working properly, the backup ASG also transmits services, which is counterproductive to VRRP redundancy backup implementation. Association between direct routes and the VRRP group can be configured to ensure path consistency.
On the NodeB side, the direct network segment routes of ASG VRRP interfaces can be associated with VRRP status. The route with the master ASG as the next hop has a lower cost than the route with the backup ASG as the next hop. The dynamic routing protocol imports the direct routes and selects the route with a lower cost, ensuring path consistency. Implementation on the RNC side is similar to that on the NodeB side.