Dynamic DNS
Related Concepts
- Dynamic DNS: Client programs, such as ping and tracert, access the DNS server using the resolver of the DNS client.
- Resolver: A server that provides mappings between domain names and IP addresses and handles a user's request for domain name resolution.
- Recursive resolution: If a DNS server cannot find the IP address corresponding to a domain name, the DNS server turns to other DNS servers for help and sends the resolved IP address to the DNS client.
- Query types:
- Class-A query: a query used to request the IPv4 address corresponding to a domain name.
- Class-AAAA query: a query used to request the IPv6 address corresponding to a domain name.
- PTR query: a query used to request the domain name corresponding to an IP address.
Implementation
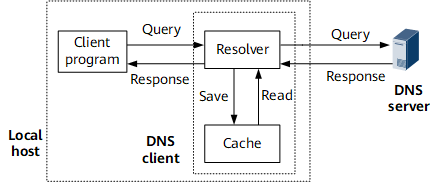
Dynamic DNS is implemented using the DNS server. Figure 1 shows the relationships between the client program, resolver, DNS server, and cache.
The DNS client is composed of the resolver and cache and is responsible for accepting and responding to DNS queries from client programs. Generally, the client program, cache, and resolver are on the same host, whereas the DNS server is on another host.
A client program, such as a ping or tracert program, sends a DNS request carrying a domain name to the DNS client.
After receiving the request, the DNS client searches the local database or the cache. If the required DNS entry is not found, the DNS client sends a query packet to the DNS server. Currently, devices support Class-A, Class-AAAA, and PTR queries.
The DNS server searches its local database for the IP address corresponding to the domain name carried in the query packet. If the corresponding IP address cannot be found, the DNS server forwards the query packet to the upper-level DNS server for help. The upper-level DNS server resolves the domain name in recursive resolution mode, as specified in the query packet, and returns the resolution result to the DNS server. The DNS server then sends the result to the DNS client.
After receiving the response packet from the DNS server, the DNS client sends the resolution result to the client program.

Dynamic DNS allows you to define a domain name suffix list by pre-configuring some domain name suffixes. After you enter a partial domain name, the DNS server automatically displays the complete domain name with different suffixes for resolution.
Usage Scenario
Dynamic DNS is used in scenarios in which a large number of mappings between domain names and IP addresses exist and these mappings change frequently.
Benefits
If a large number of mappings between domain names and IP addresses exist, manually configuring DNS entries on each DNS server is laborious. To solve this problem, use dynamic DNS instead. Dynamic DNS effectively improves configuration efficiency and facilitates DNS management.