Seamless MPLS Applications in VPN Services
Service Overview
With the growth of third generation of mobile telecommunications (3G) and Long Term Evolution (LTE) services, inter-AS leased line services becomes the key services. To carry these services over VPNs, seamless MPLS establishes an E2E LSP between a cell site gateway (CSG) and a mobile aggregate service gateway (MASG) to transmit virtual private network (VPN) services, as well as helps carriers reduce costs of network construction, operation, and maintenance. Seamless MPLS also allows carriers to uniformly operate and maintain networks.
Networking Description
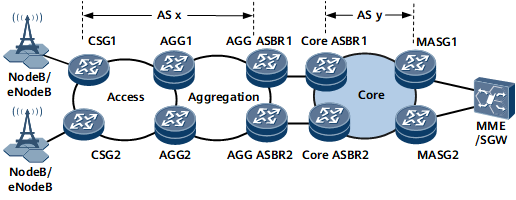
Figure 1 illustrates an LTE network. The access and aggregation layers belong to one AS, and the core layer belongs to another AS. To transmit VPN services, the inter-AS seamless MPLS+HVPN networking can be used to establish an LSP between each pair of a CSG and MASG. CSGs are connected to NodeBs that are Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) 3G base stations and eNodeBs that are LTE base stations. MASGs are connected to a mobility management entity (MME) or service gateway (SGW). VPN instances can be configured between CSGs and MASGs to transmit various types of services. An HVPN is deployed between each pair of a CSG and aggregation (AGG) node, and an inter-AS LSP is established between each pair of an AGG and MASG using the seamless MPLS technique. A NodeB or an eNodeB can then communicate with the MME or SGW.
Seamless MPLS Networking Characteristics
Requirement |
Inter-AS Seamless MPLS+HVPN |
|---|---|
Services |
Segment tunnels are established.
|
Route control |
The number of routes is minimized:
|
Enterprise leased line services |
The large-scale enterprise VPN services can be provisioned. The Layer 2 and Layer 3 leased lines connected to CSGs are easily deployed. |
Protection switching |
The following protection switching functions can be configured:
|
CSG performance requirements |
CSGs that maintain a few routes only need to process packets each with two labels. |