PIM-SSM Intra-domain
Both Protocol Independent Multicast-Source-Specific Multicast (PIM-SSM) and PIM-SM are for use on large-scale networks where group members are sparsely distributed. Unlike PIM-SM, PIM-SSM can be used in scenarios in which users know the multicast source location before they join a specific group and send requests to specific sources for multicast data. This section describes PIM-SSM intra-domain networking.
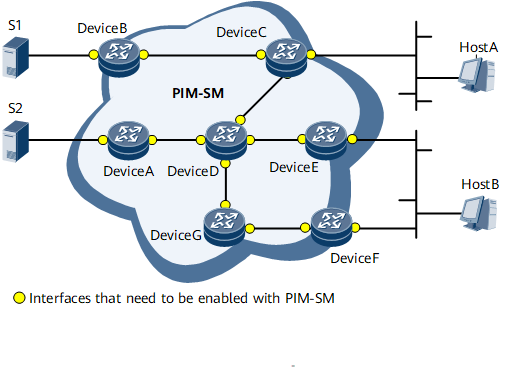
Multicast services are deployed on the large-scale network shown in Figure 1. An IGP has been deployed, and each network segment route is reachable. Group members are sparsely distributed on the network. User hosts on the network want to send Join messages directly to specific multicast sources and receive VoD information.
Implementation Solution
On the network shown in Figure 1, Hosts A and B are multicast information receivers, each located on a different leaf network. The hosts receive VoD information in multicast mode. PIM-SSM is used throughout the PIM domain. Device B is connected to multicast source S1. Device A is connected to multicast source S2. Device C is connected to Host A. Devices E and F are connected to Host B.
PIM-SSM is enabled on all router interfaces.

A receiver in a PIM-SSM scenario can send a Join message directly to a specific multicast source. A shortest path tree (SPT) is established between the multicast source and receiver, not requiring the network to maintain Rendezvous Points (RPs).
IGMP runs between Device C and Host A, between Device E and Host B, and between Device F and Host B.
When configuring IGMP on router interfaces, ensure that interface parameters are consistent. All routers connected to the same network must run the same IGMP version (IGMPv2 is recommended) and be configured with the same interface parameter values, such as the Query timer value and hold time of memberships. If the IGMP versions or interface parameters are different, IGMP group memberships are inconsistent on different routers.
Host A can send Join messages to S1. Host B can send Join messages to S2. Information sent by these multicast sources can reach user hosts.

Configuring interfaces on network edge devices to statically join all multicast groups is recommended to increase the speed for changing channels and to provide a stable viewing environment for users.