SNMPv1 Principles
SNMP defines five types of protocol data units (PDUs), also called SNMP messages, exchanged between the workstation and agent.
Get-Request PDUs: Generated and transmitted by the workstation to obtain one or more parameter values from an agent.
Get-Next-Request PDUs: Generated and transmitted by the workstation to obtain parameter values in alphabetical order from an agent.
Set-Request PDUs: Used to set one or more parameter values for an agent.
Get-Response PDUs: Contains one or more parameters. Generated by an agent and transmitted in reply to a Get-Request PDU from the workstation.
Traps: Messages that originate with an agent and are sent to inform the workstation of network events.
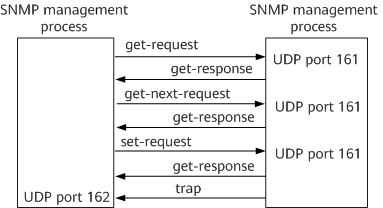
Get-Request, Get-Next-Request, and Set-Request PDUs are sent by the workstation to an agent; Get-Response PDUs and traps are sent by an agent to the workstation. When Get-Request PDUs, Get-Next-Request PDUs, and Set-Request PDUs are generated and transmitted, naming is simplified to Get, Get-Next, and Set for convenience. Figure 1 shows how the five types of PDUs are transmitted.

By default, an agent uses port 161 to receive Get, Get-Next, and Set messages, and the workstation uses port 162 to receive traps.
An SNMP message consists of a common SNMP header, a Get/Set header, a trap header, and variable binding.
Common SNMP Header
A common SNMP header has the following fields:
Version
Specifies the SNMP version. In an SNMPv1 packet, the value of this field is 0.
Community
The community is a simple text password shared by the workstation and an agent. It is a string. A common value is the 6-character string "public".
PDU type
There are five types of PDUs in total, as shown in Table 1.
Get/Set Header
The Get or Set header contains the following fields:
Request ID
An integer set by the workstation, it is carried in Get-Request messages sent by the workstation and in Get-Response messages returned by an agent. The workstation can send Get messages to multiple agents simultaneously. All Get messages are transmitted using UDP. A response to the request message sent first may be the last to arrive. In such cases, Request IDs carried in the Get-Response messages enable the workstation to identify the returned messages.
Error status
An agent enters a value in this field of a Get-Response message to specify an error, as listed in Table 2.
Value |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
0 |
noError |
No error exists. |
1 |
tooBig |
The agent cannot encapsulate its response in an SNMP message. |
2 |
noSuchName |
A nonexistent variable is contained in a message. |
3 |
badValue |
A Set operation has returned an invalid value or syntax. |
4 |
readOnly |
The workstation has attempted to modify a read-only variable. |
5 |
genErr |
Other errors. |
Error index
When noSuchName, badValue, and readOnly errors occur, the agent sets an integer in the Response message to specify an offset value for the faulty variable in the list. By default, the offset value in get-request messages is 0.
Variable binding (variable-bindings)
A variable binding specifies the variable name and corresponding value, which is empty in Get or Get-Next messages.
Trap Header
Enterprise
This field is an object identifier of a network device that sends traps. The object identifier resides in the sub-tree of the enterprise object {1.3.6.1.4.1} in the object naming tree.
Generic trap type
Table 3 lists the generic trap types that can be received by SNMP.
Value |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
0 |
coldStart |
A coldStart trap signifies that the SNMP entity, supporting a notification originator application, is reinitializing itself and that its configuration may have been altered. |
1 |
warmStart |
A warmStart trap signifies that the SNMP entity, supporting a notification originator application, is reinitializing itself such that its configuration is unaltered. |
2 |
linkDown |
An interface has changed from the Up state to the Down state. |
3 |
linkUp |
An interface has changed from the Down state to the Up state. |
4 |
authenticationFailure |
The SNMP workstation has received an invalid community name. |
5 |
egpNeighborLoss |
An EGP peer has changed to the Down state. |
6 |
enterpriseSpecific |
An event defined by the agent and specified by a code. |
To send a type 2, 3, or 5 trap, you must use the first variable in the trap's variable binding field to identify the interface responding to the trap.
Specific-code
If an agent sends a type 6 trap, the value in the Specific-code field specifies an event defined by the agent. If the trap type is not 6, this field value is 0.
Timestamp
This specifies the duration from when an agent is initializing to when an event reported by a trap occurs. This value is expressed in 10 ms. For example, a timestamp of 1908 means that an event occurred 19080 ms after initialization of the agent.