IP Forwarding on a Termination Sub-interface
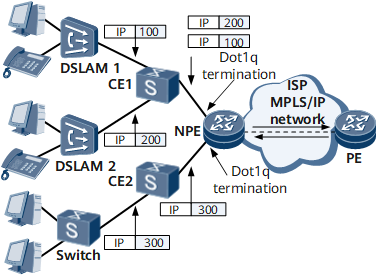
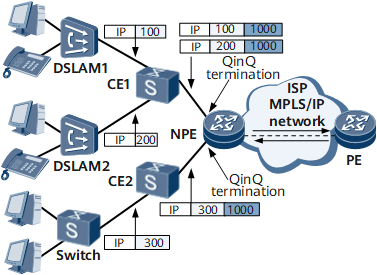
On the network shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, when the NPE at the edge of the MPLS/IP core network acts as a gateway for users, termination sub-interfaces must support IP forwarding.
IP forwarding can be configured on a sub-interface for Dot1q VLAN tag termination or sub-interface for QinQ VLAN tag termination, based on whether the user packets received by the NPE carry one or two VLAN tags.
If the user packets contain one tag, the sub-interface that has IP forwarding configured is a sub-interface for Dot1q VLAN tag termination.
If the user packets contain double tags, the sub-interface that has IP forwarding configured is a sub-interface for QinQ VLAN tag termination.
IP Forwarding on a Sub-interface for Dot1q VLAN Tag Termination
The sub-interface for Dot1q VLAN tag termination first identifies the outer VLAN tag and then generates an ARP entry containing the IP address, MAC address, and outer VLAN tag.
For the upstream traffic, the termination sub-interface strips the Ethernet frame header (including MAC address) and the outer VLAN tag, and searches the routing table to perform Layer 3 forwarding based on the destination IP address.
For the downstream traffic, the termination sub-interface encapsulates IP packets with the Ethernet frame header (including MAC address) and outer VLAN tag according to ARP entries and then sends IP packets to the target user.
IP Forwarding on a Sub-interface for QinQ VLAN Tag Termination
The sub-interface for QinQ VLAN tag termination first identifies double VLAN tags and then generates an ARP entry containing the IP address, MAC address, and double VLAN tags.
For the upstream traffic, the termination sub-interface strips the Ethernet frame header (including MAC address) and double VLAN tags, and searches the routing table to perform Layer 3 forwarding based on the destination IP address.
For the downstream traffic, the termination sub-interface encapsulates IP packets with the Ethernet frame header (including MAC address) and double VLAN tags according to ARP entries and then sends IP packets to the target user.