Application of Layer 2 Multicast for IPTV Services
Service Overview
IPTV services are video services provided for users through an IP network. IPTV services pose high requirements for bandwidth, real-time transmission, and reliability on IP MANs. Multiple users can receive the same IPTV service data simultaneously.
Given the characteristics of IPTV, multicast technologies can be used to bear IPTV services. Compared with traditional unicast, multicast ensures that network bandwidth demands do not increase with the number of users and reduces the workload of video servers and the bearer network. If service providers want to deploy IPTV services in a rapid and economical way, E2E multicast push is recommended.
Network Description
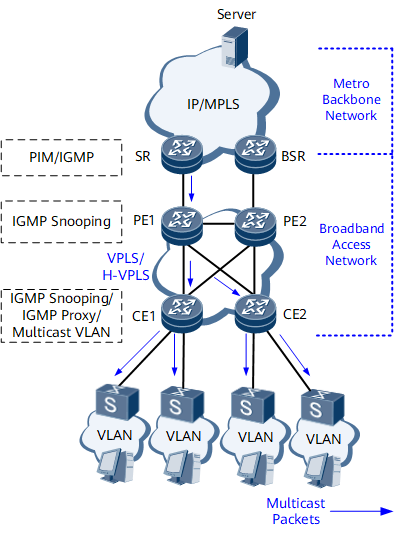
Currently, the IP MAN consists of a metro backbone network and broadband access network. IPTV service traffic is pushed to user terminals through the metro backbone network and broadband access network in sequence. Figure 1 shows an E2E IPTV service push model. The metro backbone network is mainly composed of network layer (Layer 3) devices. PIM such as PIM-SM is used on each device on the metro backbone to connect to the multicast source and IGMP is used on the devices directly connected to the broadband access network to forward multicast packets to user terminals. The broadband access network is mainly composed of data link layer (Layer 2) devices. Layer 2 multicast techniques such as IGMP proxy or IGMP snooping can be used on Layer 2 devices to forward multicast packets to terminal users.
The following section describes Layer 2 multicast features used on the broadband access network.
Feature Deployment
The broadband access network is constructed using Layer 2 devices. Layer 2 devices exchange or forward data frames by MAC address. They have week IP packet parsing and routing capabilities. As a result, the Layer 2 devices do not support Layer 3 multicast protocols. Previously, Layer 2 devices broadcast IPTV multicast traffic to all interfaces, which easily results in broadcast storms.
Deploy IGMP snooping on all Layer 2 devices, so that they listen to IGMP messages exchanged between Layer 3 devices and user terminals and maintain multicast group memberships, implementing on-demand multicast traffic forwarding.
Deploy IGMP snooping proxy on CEs close to user terminals, so that the CEs listen to, filter, and forward IGMP messages. This reduces the number of multicast protocol packets directly exchanged between CEs and upstream devices, and reduces packet processing pressure on upstream devices.
Deploy multicast VLAN= on CEs close to user terminals to reduce the network bandwidth required for transmissions between CEs and multicast sources.
The following features can also be deployed on Layer 2 devices:
VSI or VLAN-based Layer 2 multicast instance (a multicast VLAN enhancement) can be deployed on CEs close to user terminals to reduce the network bandwidth required for transmissions between CEs and multicast sources.
If the number of user terminals attached to a CE exceeds the number of IPTV channels, static multicast groups can be configured on the CE to increase the channel change speed and improve the QoS for IPTV services.
If user hosts support IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 only, SSM mapping can be deployed on the CE connected to these user terminals so the user hosts can access SSM services.
Rapid multicast traffic forwarding can be deployed on a backup PE to improve the reliability of links between the PE and CE.
- If a Layer 2 device uses no Layer 2 multicast forwarding technology, the device forwards multicast packets to all IPTV users. Broadcasting multicast packets for five IPTV channels leads to network congestion. This is the case even if the bandwidth of the interface connecting the Layer 2 device to users is 10 Mbit/s.
- After Layer 2 multicast forwarding technologies are used on the Layer 2 device, the Layer 2 device sends multicast packets only to users that require the multicast packets. If each interface of the Layer 2 device is connected to at least one IPTV user terminal, multicast packets (2 Mbit/s traffic) for at most one BTV channel are forwarded to corresponding interfaces. This ensures the availability of adequate network bandwidth and the quality of user experience.