Overview of BGP/MPLS IP VPN
Definition
A BGP/MPLS IP VPN is a Layer 3 virtual private network (L3VPN), which uses BGP to advertise VPN routes and uses MPLS to forward VPN packets on the IP backbone networks of service providers (SPs).
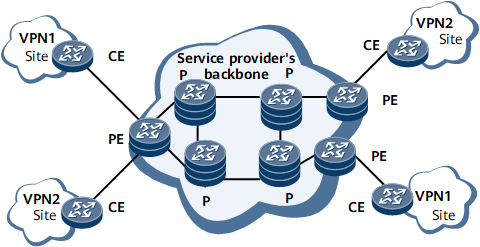
As shown in Figure 1, a BGP/MPLS IP VPN consists of the following roles:
CE: An edge device on a customer network. A CE provides interfaces that are directly connected to the SP network. A CE can be a router, a switch, or a host. Usually, a CE is unaware of the VPN and does not need to support MPLS.
PE: An edge device on an SP network. A PE is directly connected to a CE. On an MPLS network, PEs process all VPN services. The requirements on the performance of PEs are rather high.
P: A backbone device on an SP network. A P is not directly connected to a CE. Ps only need to possess basic MPLS forwarding capabilities and do not maintain VPN information.
PEs and Ps are managed by SPs. CEs are managed by users, except that the users trust SPs with the management rights.
A PE can connect to multiple CEs. A CE can connect to multiple PEs of the same SP or of different SPs.
Purpose
MPLS seamlessly integrates the flexibility of IP routing and simplicity of ATM label switching. A connection-oriented control plane is introduced into an MPLS IP network, which enriches the means of managing and operating the network. On IP networks, MPLS TE has become an important tool in managing network traffic, reducing network congestion, and ensuring QoS.
The VPNs using MPLS IP networks as the backbone networks are highly valued by carriers, and have become an important means of providing value-added services.
Unlike the IGP, BGP focuses on controlling route transmission and choosing optimal routes instead of discovering and calculating routes. VPNs use public networks to transmit VPN data, and the public networks use an IGP to discover and calculate their routes. The key to constructing a VPN is to control the transmission of VPN routes and choose the optimal routes between two PEs.
BGP uses TCP (with port number 179) as the transport layer protocol, enhancing transmission reliability. VPN routes can be directly exchanged between two PEs with routers located between them.
BGP can append any information to a route as optional BGP attributes. The information is transparently forwarded by BGP devices that cannot identify those attributes. Therefore, VPN routes can be conveniently transmitted between PEs.
When routes are updated, BGP sends only updated routes rather than all routes. This implementation saves the bandwidth consumed by route transmission, making the transmission of a great number of routes over a public network possible.
As an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP), BGP is best suited for VPNs that cross the networks of multiple carriers.