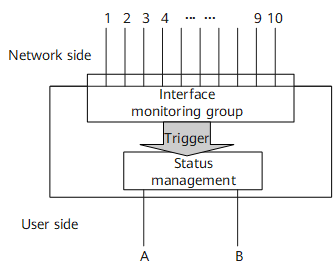
Interface Monitoring Group
Network-side interfaces can be added to an interface monitoring group. Each interface monitoring group is identified by a unique group name. The network-side interface to be monitored is a binding interface, and the user-side interface associated with the group is a track interface, whose status changes with the binding interface status. The interface monitoring group monitors the status of all binding interfaces. When a specific proportion of binding interfaces goes Down, the track interface associated with the interface monitoring group goes Down, which causes traffic to be switched from the master link to the backup link. When the number of Down binding interfaces falls below a specific threshold, the track interface goes Up, and traffic is switched back to the master link.
In the example network shown in Figure 1, ten binding interfaces are located on the network side, and two track interfaces are located on the user side. You can set a Down weight for each binding interface and a Down weight threshold for each track interface. For example, the Down weight of each binding interface is set to 10, and the Down weight thresholds of track interfaces A and B are set to 20 and 80, respectively. When the number of Down binding interfaces in the interface monitoring group increases to 2, the system automatically instructs track interface A to go Down. When the number of Down binding interfaces in the interface monitoring group increases to 8, the system automatically instructs track interface B to go Down. When the number of Down binding interfaces in the interface monitoring group falls below 8, track interface B automatically goes Up. When the number of Down binding interfaces in the interface monitoring group falls below 2, track interface A automatically goes Up.