Peer Group and Dynamic BGP Peer Group
A peer group is a set of peers with the same policies. After a peer is added to a peer group, the peer inherits the configurations of this peer group. If the configurations of the peer group change, the configurations of all the peers in the group change accordingly. A large number of BGP peers may exist on a large-scale BGP network. If many of the BGP peers need the same policies, some commands need to be run repeatedly for each peer. To simplify the configuration, you can configure a static peer group. Each peer in a peer group can be configured with unique policies to advertise and receive routes.
However, multiple BGP peers can change frequently on some BGP networks, causing the establishment of BGP peer relationships to change accordingly. If you configure peers in static mode, you must frequently add or delete peer configurations on the local device, which increases the maintenance workload. To address this problem, configure the dynamic BGP peer function to enable BGP to listen for BGP connection requests from a specified network segment, dynamically establish BGP peer relationships, and add these peers to the same dynamic peer group. This spares you from adding or deleting BGP peer configurations in response to each change in dynamic peers.
Application
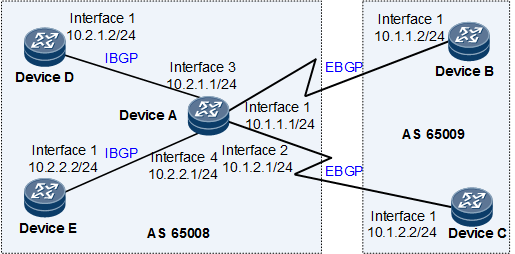
On the network shown in Figure 1, an EBGP peer relationship is established between Device A and Device B and between Device A and Device C, and an IBGP peer relationship is established between Device A and Device D and between Device A and Device E.
Device B and Device C are on the same network segment (10.1.0.0/16). In this case, you can configure a dynamic peer group on Device A to listen for BGP connection requests from this network segment. After the dynamic peer group is configured, Device B and Device C are dynamically added to this peer group, and the devices to be deployed on this network segment will also be dynamically added to the peer group when they request to establish BGP peer relationships with Device A. This process helps reduce the network maintenance workload. In addition, you can configure another dynamic peer group on Device A so that Device D and Device E are dynamically added to this peer group.