LDP Bit Error Detection
The LDP bit error detection function detects bit errors on LDP interfaces and LDP LSPs and transmits the LSP bit error rate to services carried by LDP LSPs, triggering a primary/backup LSP switchover. This function prevents service transmission quality from deteriorating and improves network reliability.
Background
As mobile services evolve from narrowband voice services to integrated broadband services, providing rich voice, streaming media, and high speed downlink packet access (HSDPA) services, the demand for network bandwidth is rapidly increasing. Meeting the bandwidth demand on traditional bearer networks requires huge investments. Therefore, carriers are in urgent need of an access mode that is low cost, flexible, and highly efficient, which can help them meet the challenges brought by the growth in wideband services. In this context, the all-IP mobile bearer networks are an effective means of dealing with these issues. IP radio access networks (RANs), a type of IP-based mobile bearer network, are increasingly widely used.
IP RANs, however, have more complex reliability requirements than traditional bearer networks when carrying broadband services. Traditional fault detection mechanisms cannot trigger protection switching based on random bit errors. Therefore, bit errors may degrade or even interrupt services on an IP RAN in extreme cases. Bit-error-triggered protection switching can solve this problem.
Benefits
Bit-error-triggered LDP protection switching has the following benefits:
Protects traffic from random bit errors, improving service quality.
Enables devices to record bit error events, enabling carriers to quickly locate the nodes or lines with bit errors and take corrective measures.
Related Concepts
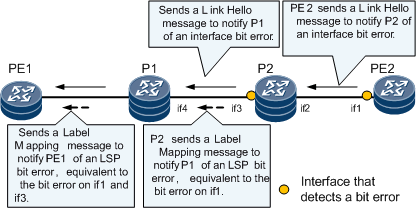
LDP interface bit error rate
LDP interface bit error rate is the bit error rate detected by LDP on an interface. A node uses a Link Hello message to report its LDP interface bit error rate to an upstream LDP peer.
LSP bit error rate
LSP bit error rate on a node = LSP bit error rate reported by the downstream LDP peer + the LDP interface bit error rate reported by the downstream LDP peer.
Implementation

LDP only detects and transmits bit errors, and service switching such as in PW switching or L3VPN route switching occurs on paths carried over LDP.