OSPF LSA Format
Each router in an AS generates one or more types of LSAs, depending on the router's type. Multiple LSAs form an LSDB. OSPF encapsulates routing information into LSAs for transmission. Commonly used LSAs include:
Summary-LSA, including network-summary-LSAs and ASBR-summary-LSAs
LSA Header Format
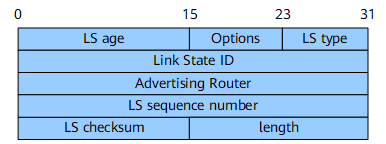
All LSAs have the same header. Figure 1 shows an LSA header.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
LS age |
16 bits |
Time that elapses after an LSA is generated, in seconds. The value of this field continually increases regardless of whether the LSA is transmitted over a link or saved in an LSDB. |
Options |
8 bits |
The values are as follows:
|
LS type |
8 bits |
Type of the LSA. The values are as follows:
|
Link State ID |
32 bits |
This field together with the LS type field describes an LSA in an AS. |
Advertising Router |
32 bits |
Router ID of the router that generates the LSA. |
LS sequence number |
32 bits |
Sequence number of the LSA. routers can use this field to identify the latest LSA. |
LS checksum |
16 bits |
Checksum of all fields except the LS age field. |
length |
16 bits |
Length of the LSA including the LSA header, in bytes. |
Router-LSA
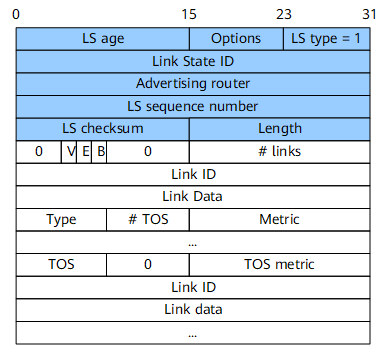
A router-LSA (Type 1) describes the link status and cost of a router. Router-LSAs are generated by a router and advertised within the area to which the router belongs. Figure 2 shows the format of a router-LSA.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Link State ID |
32 bits |
Router ID of the device that generates the LSA. |
V (Virtual Link) |
1 bit |
If the router that generates the LSA is located at one end of a virtual link, this field is set to 1. In other cases, this field is set to 0. |
E (External) |
1 bit |
If the router that generates the LSA is an autonomous system boundary router (ASBR), this field is set to 1. In other cases, this field is set to 0. |
B (Border) |
1 bit |
If the router that generates the LSA is an area border router (ABR), this field is set to 1. In other cases, this field is set to 0. |
# links |
16 bits |
Number of links and interfaces described in the LSA, including all links and interfaces in the area to which the router belongs. |
Link ID |
32 bits |
Object to which the router is connected. Its meanings are as follows:
|
Link Data |
32 bits |
Link data. Its meanings are as follows:
|
Type |
8 bits |
Type of the router link. The values are as follows:
|
# ToS |
8 bits |
Number of types of service (ToSs). |
metric |
16 bits |
Cost of the link. |
ToS |
8 bits |
Type of service. |
ToS metric |
16 bits |
Metric for the specified ToS. |
Network-LSA
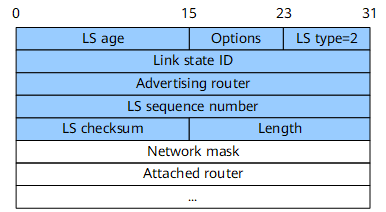
A network LSA (Type 2) describes the link status of all routers on the local network segment. Network-LSAs are generated by a DR on a broadcast or non-broadcast multiple access (NBMA) network and advertised within the area to which the DR belongs. Figure 3 shows the format of a network-LSA.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Link State ID |
32 bits |
Interface IP address of the DR |
Network Mask |
32 bits |
Mask of the broadcast or NBMA network |
Attached Router |
32 bits |
Router IDs of all routers on the broadcast or NBMA network, including the router ID of the DR |
Summary-LSA
A network-summary-LSA (Type 3) describes routes on a network segment in an area. The routes are advertised to other areas.
An ASBR-summary-LSA (Type 4) describes routes to the ASBR in an area. The routes are advertised to all areas except the area to which the ASBR belongs.
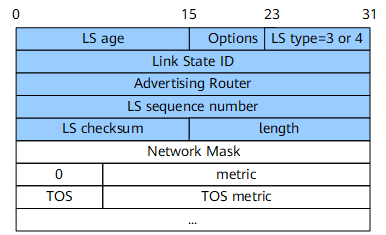
Type 3 and Type 4 LSAs have the same format and are generated by ABRs. Figure 4 shows the format of a summary-LSA.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Link State ID |
32 bits |
Advertised network address. |
Network Mask |
32 bits |
Mask of the broadcast or NBMA network |
metric |
24 bits |
Cost of the route to the destination address |
ToS |
8 bits |
Type of service. |
ToS metric |
24 bits |
Metric for the specified ToS |

When a default route is advertised, both the Link State ID and Network Mask fields are set to 0.0.0.0.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Link State ID |
32 bits |
Router ID of the ASBR |
Network Mask |
32 bits |
Set to 0.0.0.0 |
metric |
24 bits |
Cost of the route to the destination address |
ToS |
8 bits |
Type of service. |
ToS metric |
24 bits |
Metric for the specified ToS |
AS-External-LSA
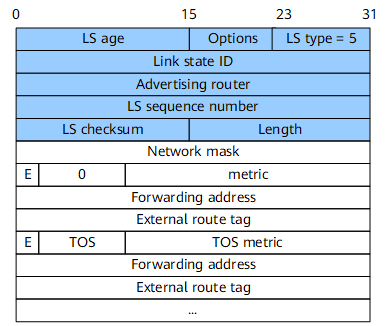
An AS-external-LSA (Type 5) describes AS external routes. AS-external-LSAs are generated by an ASBR. Among the five types of LSAs, only AS-external-LSAs can be advertised to all areas except stub areas and not-so-stubby areas (NSSAs). Figure 5 shows the format of an AS-external-LSA.
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Link State ID |
32 bits |
Advertised network address. |
Network Mask |
32 bits |
Mask of the advertised destination address. |
E |
1 bit |
Type of the external route. The values are as follows:
|
metric |
24 bits |
Cost of the route to the destination address |
Forwarding Address |
32 bits |
Packets destined for the advertised destination address are forwarded to the address specified by this field. |
External Route Tag |
32 bits |
Tag added to the external route. This field can be used to manage external routes. OSPF itself does not use this field. |
ToS |
8 bits |
Type of service. |
ToS metric |
24 bits |
Metric for the specified ToS. |