Hub & Spoke
The Hub & Spoke networking can be used to enable an access control device on a VPN to control the mutual access of other users. The site where the access control device locates is called a Hub site, and other sites are called Spoke sites. At the Hub site, a device that accesses the VPN backbone network is called a Hub-CE; at a Spoke site, a device that accesses the VPN backbone network is called a Spoke-CE. On the VPN backbone network, a device that accesses the Hub site is called a Hub-PE; a device that accesses a Spoke site is called a Spoke-PE.
A Spoke site advertises routes to the Hub site, and the Hub site then advertises the routes to other Spoke sites. No direct route exists between the Spoke sites. The Hub site controls the communication between the Spoke sites.
In the Hub & Spoke networking model, two VPN targets are configured to stand for Hub and Spoke respectively.
The configuration of a VPN target on a PE must comply with the following rules:
The export target and the import target of the Spoke-PE at a Spoke site are Spoke and Hub respectively. The import target of a Spoke-PE is different from the export targets of other Spoke-PEs.
A Hub-PE requires two interfaces or sub-interfaces. One interface or sub-interface receives routes from Spoke-PEs, and the import target of the VPN instance on the interface is Spoke. The other interface or sub-interface advertises the routes to Spoke-PEs, and the export target of the VPN instance on the interface is Hub.
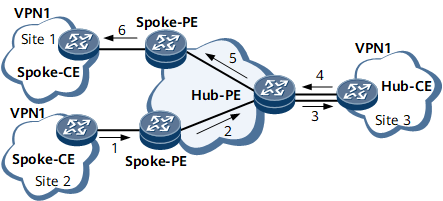
As shown in Figure 1, the communication between Spoke sites is controlled by the Hub site. The lines with arrowheads show the process of advertising a route from Site 2 to Site 1.
The Hub-PE can receive the VPN-IPv4 routes advertised by all the Spoke-PEs.
All the Spoke-PEs can receive the VPN-IPv4 routes advertised by the Hub-PE.
The Hub-PE advertises the routes learned from the Spoke-PEs to the Hub-CE, and advertises the routes learned from the Hub-CE to all the Spoke-PEs. The Spoke sites can access each other through the Hub site.
The import target of a Spoke-PE is different from the export targets of other Spoke-PEs. Two Spoke-PEs cannot directly advertise VPN-IPv4 routes to each other. As a result, the Spoke sites cannot access each other.
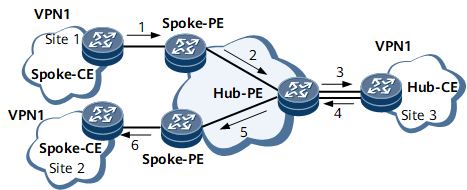
The transmission path between Site 1 and Site 2 is shown in Figure 2. The lines with arrowheads indicate the path from Site 2 to Site 1.
Networking Description
Hub & Spoke networking schemes include:
External Border Gateway Protocol (EBGP) running between the Hub-CE and Hub-PE, and between Spoke-PEs and Spoke-CEs
IGP running between the Hub-CE and Hub-PE, and between Spoke-PEs and Spoke-CEs
EBGP running between the Hub-CE and Hub-PE, and IGP running between Spoke-PEs and Spoke-CEs
The following describes these networking schemes in detail:
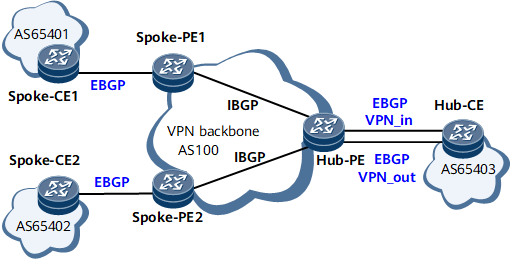
EBGP running between the Hub-CE and Hub-PE, and between Spoke-PEs and Spoke-CEs
As shown in Figure 3, the routing information advertised by a Spoke-CE is forwarded to the Hub-CE before being transmitted to other Spoke-PEs. If EBGP runs between the Hub-PE and Hub-CE, the Hub-PE performs the AS-Loop check on the route. If the Hub-PE detects its own AS number in the route, it discards the route. In this case, to implement the Hub & Spoke networking, the Hub-PE must be configured to permit the existence of repeated local AS numbers.
IGP running between the Hub-CE and Hub-PE, and between Spoke-PEs and Spoke-CEs
Figure 4 IGP running between the Hub-CE and Hub-PE, and between Spoke-PEs and Spoke-CEs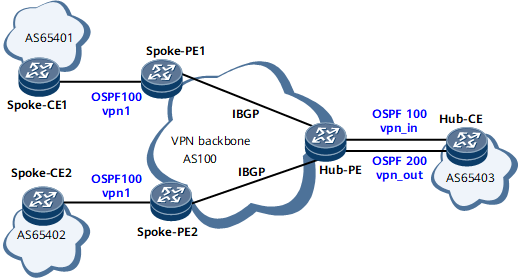
Because all PEs and CEs exchange routing information through IGP and IGP routes do not contain the AS_Path attribute, the AS_Path field of BGP VPNv4 routes is null.
EBGP running between the Hub-CE and Hub-PE, and IGP running between Spoke-PEs and Spoke-CEs
Figure 5 EBGP running between the Hub-CE and Hub-PE, and IGP running between Spoke-PEs and Spoke-CEs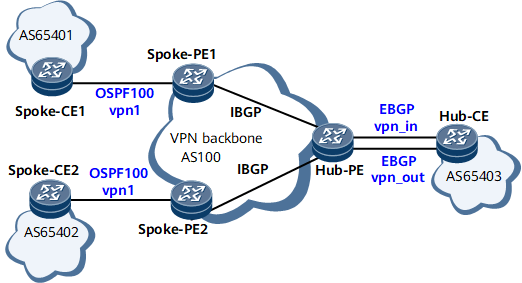
The networking topology is similar to that shown in Figure 3. The AS_Path attribute of the route forwarded by the Hub-CE to the Hub-PE contains the AS number of the Hub-PE. Therefore, the Hub-PE must be configured to permit the existence of repeated local AS numbers.