Fault Information Advertisement Between CFM and Other Modules
Fault Information Advertisement Between CFM and Detection Modules
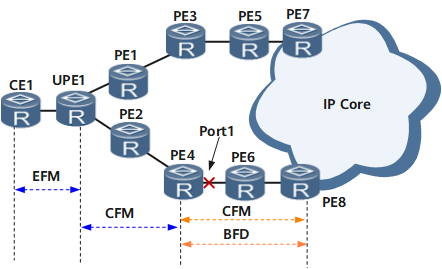
An OAMMGR module associates CFM with detection modules. A detection module can be EFM, CFM, BFD. Fault information advertisement between CFM and detection modules enables a device to delete ARP or MAC address entries once a fault is detected. Figure 1 shows the network on which fault information is advertised between CFM and detection modules.
The following example illustrates fault information advertisement between CFM and detection modules over a path UPE1 -> PE2 -> PE4 -> PE6 -> PE8 on the network shown in Table 1.
Function Deployment |
Issue to Be Resolved |
Solution |
|---|---|---|
CFM is used to monitor the link between UPE1 and PE4. |
Although CFM detects a fault in the link between UPE1 and PE4, CFM cannot notify PE6 of the fault. As a result, PE6 still forwards network traffic to PE4, causing a traffic interruption. Although port 1 on PE4 goes Down, port 1 cannot notify CE1 of the fault. As a result, CE1 still forwards user traffic to PE4, causing a traffic interruption. |
CFM can be associated with port 1.
The association between CFM and a port is used to detect faults in an active link of a link aggregation group or in the link aggregation group in 1:1 active/standby mode. If a fault is detected, a protection switchover is triggered. |
EFM is used to monitor the direct link between CE1 and UPE1, and CFM is used to monitor the link between UPE1 and PE4. |
Although CFM detects a fault, CFM cannot notify CE1 of the fault. As a result, CE1 still forwards user traffic to PE4, causing a traffic interruption. |
The EFM module can be associated with the CFM module.
|
CFM is configured to monitor the links between UPE1 and PE4 and between PE4 and PE8. |
|
|
|
|
The CFM module can be associated with the BFD module.
|
Fault Information Advertisement Between CFM and Application Modules
The OAMMGR module associates a CFM module with application modules, such as a Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) module.
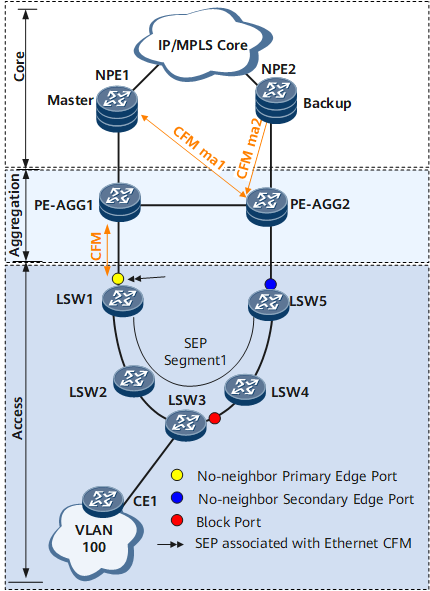
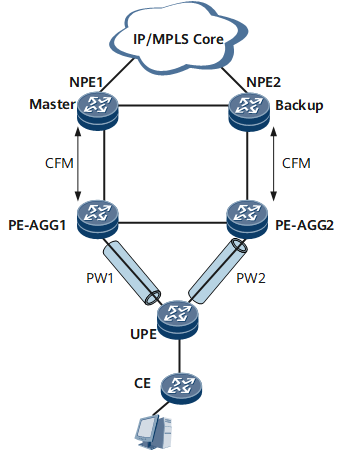
Figure 2 shows the network on which a CFM module advertises fault information to a VRRP module. Figure 3 shows the network on which a VRRP module advertises fault information to a CFM module.
Table 2 describes fault information advertisement between CFM and VRRP modules.
Function Deployment |
Issue to Be Resolved |
Solution |
|---|---|---|
|
If a fault occurs on the link between NPE1 (the master) and PE-AGG1, NPE2 cannot receive VRRP packets within a period of three times the interval at which VRRP packets are sent. NPE2 then preempts the Master state. As a result, two master devices coexist in a VRRP backup group, and the UPE receives double copies of network traffic. |
CFM can be associated with the VRRP module on NPEs. If CFM detects a fault in the link between PE-AGG1 and NPE1, it instructs the OAMMGR module to notify the VRRP module of the fault. After receiving the notification, the VRRP module triggers a master/backup VRRP switchover. NPE1 then changes its VRRP status to Initialize. NPE2 changes its VRRP status from Backup to Master after a period of three times the interval at which VRRP packets are sent. This process prevents two master devices from coexisting in the VRRP backup group. |
|
If a fault occurs on the backbone network, it triggers a master/backup VRRP switchover but cannot trigger an active/standby PW switchover. As a result, the CE still transmits user traffic to the previous master NPE, causing a traffic interruption. |
|