Application of MSTP
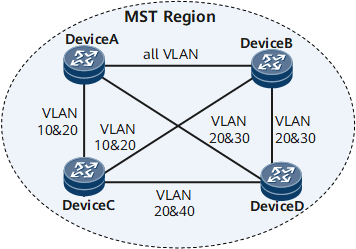
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) allows packets in different VLANs to be forwarded by using different spanning tree instances, as shown in Figure 1. The configurations are as follows:
All devices on the network belong to the same Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) region.
VLAN 10 packets are forwarded within MSTI 1; VLAN 30 packets are forwarded within MSTI 3; VLAN 40 packets are forwarded within MSTI 4; VLAN 20 packets are forwarded within MSTI 0.
On the network shown in Figure 1, Device A and Device B are aggregation-layer devices, and Device C and Device D are access-layer devices. VLAN 10 and VLAN 30 are terminated on aggregation-layer devices, and VLAN 40 is terminated on an access-layer device. Therefore, Device A and Device B can be configured as the roots of instances 1 and 3 respectively; Device C can be configured as the root of instance 4.