Overview of QinQ
Definition
802.1Q-in-802.1Q (QinQ) is a technology that adds another layer of IEEE 802.1Q tag to the 802.1Q tagged packets entering the network. This technology expands the VLAN space by tagging the tagged packets. It allows services in a private VLAN to be transparently transmitted over a public network.
Purpose
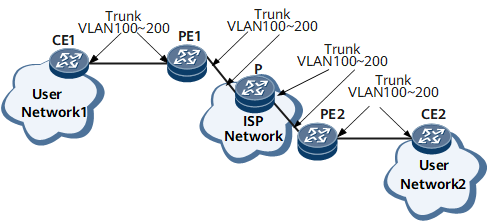
During intercommunication between Layer 2 LANs based on the traditional IEEE 802.1Q protocol, when two user networks access each other through a carrier network, the carrier must assign VLAN IDs to users of different VLANs, as shown in Figure 1. User Network1 and User Network2 access the backbone network through PE1 and PE2 of a carrier network respectively.
To connect VLAN 100 - VLAN 200 on User Network1 to VLAN 100 - VLAN 200 on User Network2, interfaces connecting CE1, PE1, the P, PE2, and CE2 can be configured to function as trunk interfaces and to allow packets from VLAN 100 - VLAN 200 to pass through.
This configuration, however, makes user VLANs visible on the backbone network and wastes the carrier's VLAN ID resources (4094 VLAN IDs are used). In addition, the carrier has to manage user VLAN IDs, and users do not have the right to plan their own VLANs.
The 12-bit VLAN tag defined in IEEE 802.1Q identifies only a maximum of 4096 VLANs, unable to isolate and identify mass users in the growing metro Ethernet (ME) network. QinQ is therefore developed to expand the VLAN space by adding another 802.1Q tag to an 802.1Q tagged packet. In this way, the number of VLANs increases to 4096 x 4096.
In addition to expanding VLAN space, QinQ is applied in other scenarios with the development of the ME network and carriers' requirements on refined operation. The outer and inner VLAN tags can be used to differentiate users from services. For example, the inner tag represents a user, while the outer tag represents a service. Moreover, QinQ functions as a simple and practical VPN technology by transparently transmitting private VLAN services over a public network. It extends services of a core MPLS VPN to the ME network and implements an end-to-end VPN.
Since the QinQ technology is easy to use, it has been widely applied on ISP networks. For example, it is used by multiple services on the metro Ethernet. As the metro Ethernet develops, different vendors propose their own metro Ethernet solutions. QinQ with its simplicity and flexibility, plays important roles in metro Ethernet solutions.
Benefits
- Extends VLANs to isolate and identify more users.
- Facilitates service deployment by allowing the inner and outer tags to represent different information. For example, use the inner tag to identify a user and the outer tag to identify a service.
- Allows ISPs to implement refined operation by providing diversified encapsulation and termination modes.