Tunnel Policy Selector
Principles
On a BGP/MPLS IP VPN in inter-AS VPN Option B or inter-AS VPN Option C mode, the VPN routes that an autonomous system boundary router (ASBR) or PE receives recurse only to LDP LSPs within an AS. Recursion is considered failed so long as LDP LSPs do not exist, no matter whether other types of tunnels exist. This implementation strictly confines the types of recursive tunnels, making network deployment inflexible. In addition, customers cannot use MPLS TE channels to guarantee the transmission quality by means of traffic engineering. To break the restriction of tunnel types, tunnel policy selectors are introduced.
Tunnel policy selectors achieve on-demand recursion by matching the route distinguisher (RD) and next hop of a route, facilitating tunnel selection. Tunnel policy selectors can use various tunnel policies for VPN routes to recurse to different types of tunnels, better meeting customer requirements.
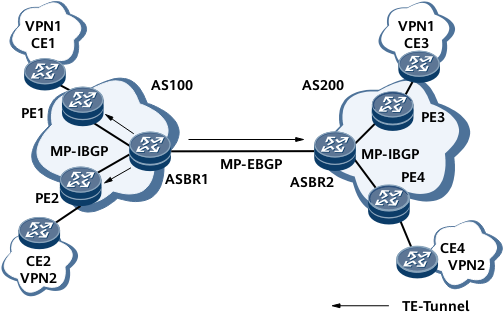
Figure 1 shows the networking diagram for a BGP/MPLS IP VPN in inter-AS VPN Option B mode.
If no tunnel policy selector is configured on ASBR1, the VPN routes received by ASBR1 can only recurse to the LDP LSP between ASBR1 and PE1, PE2, or ASBR2.
After a tunnel policy selector is configured on ASBR1, the VPN routes received by ASBR1 can recurse to any type of tunnel between ASBR1 and PE1, PE2, or ASBR2. This implementation allows flexible networking. After you configure tunnel policy selectors to select TE tunnels for route recursion, the bandwidth for data transmission can be ensured.
Implementation
A tunnel policy selector consists of one or more nodes, and the relationship between these nodes is "OR". The system checks the nodes according to index numbers. If a route matches a node in the tunnel policy selector, the route stops the matching process.
Each node comprises a set of if-match and apply clauses:
The if-match clauses define the matching rules that are used to match certain route attributes, such as the next hop and RD. The relationship between the if-match clauses of a node is "AND". A route matches a node only when the route meets all the matching rules specified by the if-match clauses of the node.
The apply clauses specify actions. When a route matches a node, the apply clauses select a corresponding tunnel policy for the route. This tunnel policy can select other types of tunnels to carry services by means of prioritizing or tunnel binding.
The node matching modes of a tunnel policy selector are as follows:
Permit: If a route matches all the if-match clauses of a node, the route matches the tunnel policy selector and all the actions defined by apply clauses are performed on the route. If a route does not match any if-match clauses of a node, the route continues to match the next node.
Deny: In this mode, the apply clauses are not implemented. If a route meets all the if-match clauses of the node, the route is denied and no longer matches other nodes of the tunnel policy selector.
Usage Scenario
Tunnel policy selectors apply to BGP/MPLS IP VPNs in inter-AS VPN Option B or inter-AS VPN Option C mode.
Benefits
- Routes can recurse to other types of tunnels besides LDP LSPs, allowing flexible networking.
- MPLS TE tunnels can be used for route recursion to support QoS.