Basic Concepts
QinQ is a technology used to expand VLAN space by adding another 802.1Q VLAN tag to a tagged 802.1Q packet. To accommodate to the ME network development, QinQ becomes diversified in its encapsulation and termination modes and is more intensely applied in service refined operation. The following describes the format of a QinQ packet, QinQ encapsulation on an interface, and QinQ termination on a sub-interface.
QinQ Packet Format
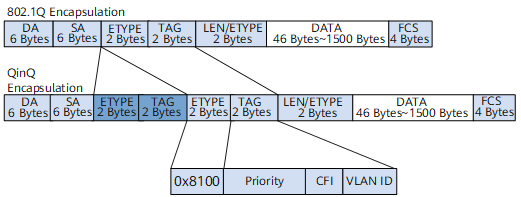
A QinQ packet has a fixed format. In the packet, another 802.1Q tag is added before an 802.1Q tag. A QinQ packet is 4–byte longer than a common 802.1Q packet.
Figure 1 shows 802.1Q encapsulation.
- Inner VLAN tag: private VLAN tag that identifies the VLAN to which a user belongs.
- Outer VLAN tag: public VLAN tag that is assigned by a carrier to a user.
QinQ Encapsulation
QinQ encapsulation is to add another 802.1Q tag to a single-tagged packet. QinQ encapsulation is usually performed on UPE interfaces connecting to users.
Currently, only interface-based QinQ encapsulation is supported. Interface-based QinQ encapsulation, also known as QinQ tunneling, encapsulates packets that enter the same interface with the same outer VLAN tag. This encapsulation mode cannot flexibly distinguish between users and services.
Sub-interface for VLAN Tag Termination
- After an interface receives a packet with one or two VLAN tags, the device removes the VLAN tags and forwards the packet at Layer 3. The outbound interface decides whether to add one or two VLAN tags to the packet.
- Before an interface forwards a packet, the device adds the planned VLAN tag to the packet.
The following section describes the termination types, the VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces, and the applications of VLAN tag termination.
-
VLAN packets are classified into dot1q packets, which carry only one VLAN tag, and QinQ packets, which carry two VLAN tags. Accordingly, there are two VLAN tag termination modes:
VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces
Dot1q/QinQ termination is conducted on sub-interfaces.Sub-interface for dot1q VLAN tag termination
A sub-interface that terminates packets carrying one VLAN tag.
Sub-interface for QinQ VLAN tag termination
A sub-interface that terminates packets carrying two VLAN tags.
Sub-interfaces for QinQ VLAN tag termination are classified into the following types:- Explicit sub-interface for QinQ VLAN tag termination: The pair of VLAN tags specifies two VLANs.
- Implicit sub-interface for QinQ VLAN tag termination: The pair of VLAN tags specifies two ranges of VLANs.

Dot1q and QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces do not support transparent transmission of packets that do not contain a VLAN tag, and discard received packets that do not contain a VLAN tag.
- Applications of VLAN tag termination
-
The VLAN technology is widely used because it allows Layer 2 packets of different users to be transmitted separately. With the VLAN technology, a physical LAN is divided into multiple logical broadcast domains (VLANs). Hosts in the same VLAN can communicate with each other at Layer 2, but hosts in different VLANs cannot. The Layer 3 routing technology is required for communication between hosts in different VLANs. The following interfaces can be used to implement inter-VLAN communication:
Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces on routers
Conventional Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces do not identify VLAN packets. After receiving VLAN packets, they consider the packets invalid and discard them. To implement inter-VLAN communication, create Ethernet sub-interfaces on an Ethernet interface and configure the sub-interfaces to remove tags from VLAN packets.
Communication between devices in the LAN and WAN
Most LAN packets carry VLAN tags. Certain wide area network (WAN) protocols, such as Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), cannot identify VLAN packets. Before forwarding VLAN packets from a LAN to a WAN, a device needs to record the VLAN information carried in the VLAN packets and then remove the VLAN tags.
When a device receives packets, it adds the locally stored VLAN information to the packets and forwards them to VLAN users.
-
User-VLAN Sub-interface
User-VLAN sub-interfaces are used for user access to a BRAS. Different user-VLAN sub-interfaces can be configured on an interface for different VLAN users. After users' VLAN packets arrive on a BRAS, the BRAS can differentiate user services based on the VLAN IDs in the packets and then use proper authentication and address allocation methods for the users. After that, the BRAS sends users' VLAN packets to a RADIUS server for user location identification.
After user-VLAN sub-interfaces on a BRAS receive matching packets, they remove VLAN tags and then forward the packets at Layer 3.
- Incoming packets supported by user-VLAN sub-interfaces fall into the following categories:
Single-tagged VLAN packets
User-VLAN sub-interfaces remove the single VLAN tags and forward the packets at Layer 3.
Double-tagged VLAN packets
User-VLAN sub-interfaces remove the double VLAN tags and forward the packets at Layer 3.
The outer and inner VLAN tags in double-tagged packets identify services and users, respectively.
Any-other packets
If packets received on user-VLAN sub-interfaces are neither single-tagged nor double-tagged VLAN packets permitted by the sub-interfaces, these packets are forwarded by user-VLAN sub-interfaces of any-other type at Layer 3.

VE interfaces do not support packets of any-other type.
Usage scenario of user-VLAN sub-interfaces
An IP core network cannot identify VLAN tags in user packets. If VLAN users need to access an IP core network through a BRAS over a Layer 2 network, user-VLAN sub-interfaces can be configured on the BRAS to remove the VLAN tags. If VLAN users need to access an IP core network through a BRAS over a Layer 3 network, Dot1q or QinQ VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces can be configured on the BRAS to remove the VLAN tags.