DHCP Relay on a Termination Sub-interface
On the network shown in Figure 2 and Figure 2, the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) relay function is configured on termination sub-interfaces. This function allows the sub-interfaces to add user tag information into Option 82, so that a DHCP server can assign IP addresses based on the tag information.
The DHCP relay function can be configured on a sub-interface for Dot1q VLAN tag termination or sub-interface for QinQ VLAN tag termination, based on whether the user packets received by a PE contain one or two VLAN tags.
If the user packets contain one tag, the sub-interface that has the DHCP relay function configured is a sub-interface for Dot1q VLAN tag termination.
If the user packets contain double tags, the sub-interface that has the DHCP relay function configured is a sub-interface for QinQ VLAN tag termination.
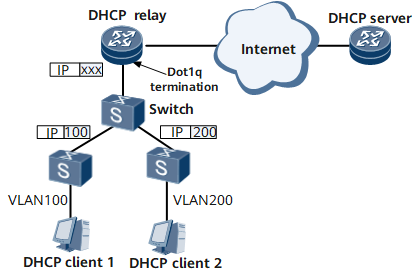
DHCP Relay on a Sub-interface for Dot1q VLAN Tag Termination
On the network shown in Figure 1, the packet received by the DHCP relay carries a single tag. If a sub-interface for Dot1q VLAN tag termination does not support the DHCP relay, the DHCP relay regards the received packet as an invalid packet and discards it. As a result, the DHCP client cannot obtain an IP address from the DHCP server.
When receiving a DHCP request message, the DHCP relay adds user tag information into the Option 82 field in the message.
When receiving a DHCP reply message (ACK message) from the DHCP server, the DHCP relay analyzes the DHCP reply and generates a binding table.
The DHCP relay checks user packets based on the user tag information.
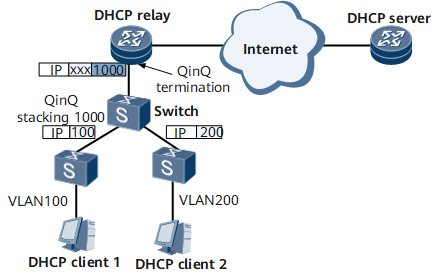
DHCP Relay on a Sub-interface for QinQ VLAN Tag Termination
On the network shown in Figure 1, the packet received by the DHCP relay carries double tags. If a sub-interface for QinQ VLAN tag termination does not support the DHCP relay, the DHCP relay regards the received packet as an invalid packet and discards it. As a result, the DHCP client cannot obtain an IP address from the DHCP server.
When receiving a DHCP request message, the DHCP relay adds user tag information into the Option 82 field in the message.
When receiving a DHCP reply message (ACK message) from the DHCP server, the DHCP relay analyzes the DHCP reply and generates a binding table.
The DHCP relay checks user packets based on the user tag information.