LDP GTSM
For an overview of GTSM, see the HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F Series Feature Description - Security.
Principles
LDP GTSM implements GTSM implementation over LDP.
To protect the router against attacks, GTSM checks the TTL in each packet to verify it. GTSM for LDP verifies LDP packets exchanged between neighbor or adjacent (based on a fixed number of hops) routers. The TTL range is configured on each router for packets from other routers, and GTSM is enabled. If the TTL of an LDP packet received by a router configured with LDP is out of the TTL range, the packet is considered invalid and discarded. Therefore, the upper layer protocols are protected.
Usage Scenario
GTSM is used to protect the TCP/IP-based control plane against CPU usage attacks, for example, CPU overload attacks. GTSM for LDP is used to verify all LDP packets to prevent LDP from suffering CPU-based attacks when LDP receives and processes a large number of forged packets.
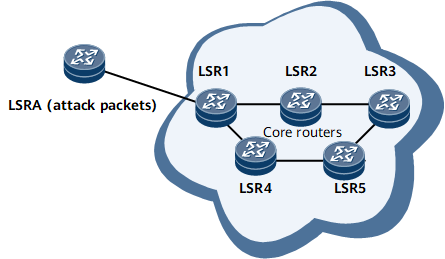
In Figure 1, LSR1 through LSR5 are core routers on the backbone network. When LSRA is connected to the router through another device, LSRA may initiate an attack by forging LDP packets that are transmitted among LSR 1 to LSR 5.
After LSRA accesses the backbone network through another device and forges a packet, the TTL carried in the forged packet cannot be forged.
A GTSM policy is configured on LSR1 through LSR5 separately and is used to verify packets reaching possible neighbors. For example, on LSR5, the valid number of hops is set to 1 or 2, and the valid TTL is set to 254 or 255 for packets sent from LSR2. The forged packet sent by LSRA to LSR5 through multiple intermediate devices contains a TTL value that is out of the preset TTL range. LSR5 discards the forged packet and prevents the attack.