Flow Sampling and Establishment
Flow Sampling
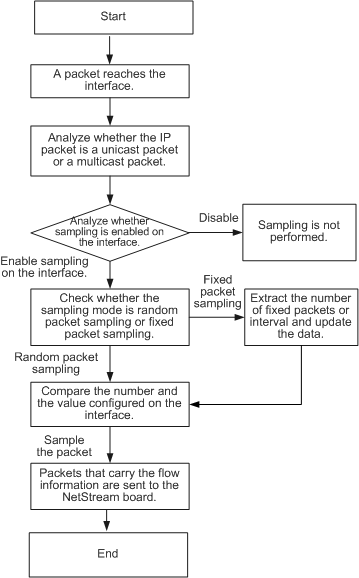
With flow sampling, information about only a few packets needs to be extracted for analysis, which reduces the impact of the NetStream function on the device performance. Figure 1 shows the NetStream sampling process.
Packet-based random sampling
One packet out of a random number of packets is sampled. For example, the sample ratio configured on a NetStream-enabled interface is M:1, and N packets out of N x M packets passing through the interface are sampled.
Packet-based regular sampling
One packet is regularly sampled at a fixed packet interval. If the packet interval is set to 100 and the fifth packet has been sampled, a device samples every 100th packet. For example, packets 105, 205, 305 are sampled.
Time-based random sampling
One packet is randomly sampled at a random interval. If the sampling time period is 100 ms, one packet is randomly sampled among packets that pass through the interface within every 100 ms.
Time-based regular sampling
One packet is regularly sampled at a fixed time interval. If the time interval is 100 ms and the first packet has been sampled at the 30th ms, the device samples packets that pass through the interface every 100 ms. For example, packets are sampled at the 130th ms, 230th ms, and 330th ms.

The NetEngine 8000 F supports three sampling modes: packet-based regular sampling, packet-based random sampling, and time-based regular sampling.
Flow Establishment
NetStream can define flows based on the 5-tuple, ToS, and inbound or outbound interface information.