RIPng Packet Format
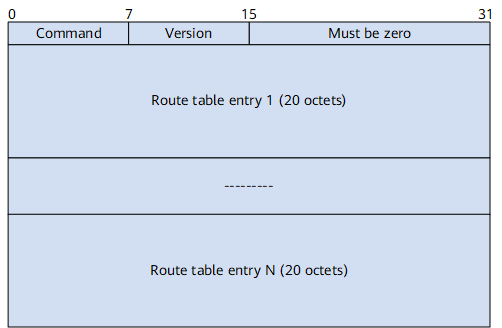
A RIPng packet is composed of a header and multiple route table entries (RTEs). In a RIPng packet, the maximum number of RTEs is determined by the maximum transmission unit (MTU) of an interface.
Figure 1 shows the basic format of a RIPng packet.
A RIPng packet contains two types of RTEs:
Next hop RTE: It defines the IPv6 address of the next hop and is located before a group of IPv6-prefix RTEs that have the same next hop. The Metric field of a next hop RTE is always 0xFF.
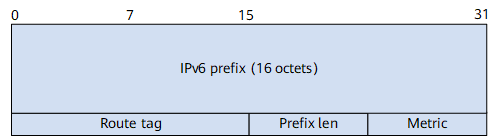
IPv6-prefix RTE: It describes the destination IPv6 address and the cost in the RIPng routing table and is located after a next hop RTE. A next hop RTE can be followed by multiple different IPv6-prefix RTEs.
Figure 2 shows the format of a next hop RTE.
Figure 3 shows the format of an IPv6-prefix RTE.